Alterations of the CIB2 calcium- and integrin-binding protein cause Usher syndrome type 1J and nonsyndromic deafness DFNB48
- PMID: 23023331
- PMCID: PMC3501259
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2426
Alterations of the CIB2 calcium- and integrin-binding protein cause Usher syndrome type 1J and nonsyndromic deafness DFNB48
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Alterations of the CIB2 calcium- and integrin-binding protein cause Usher syndrome type 1J and nonsyndromic deafness DFNB48.Nat Genet. 2025 Sep;57(9):2340-2342. doi: 10.1038/s41588-025-02332-w. Nat Genet. 2025. PMID: 40858907 No abstract available.
Abstract
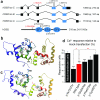
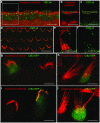
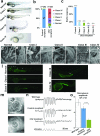
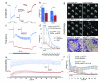
Sensorineural hearing loss is genetically heterogeneous. Here, we report that mutations in CIB2, which encodes a calcium- and integrin-binding protein, are associated with nonsyndromic deafness (DFNB48) and Usher syndrome type 1J (USH1J). One mutation in CIB2 is a prevalent cause of deafness DFNB48 in Pakistan; other CIB2 mutations contribute to deafness elsewhere in the world. In mice, CIB2 is localized to the mechanosensory stereocilia of inner ear hair cells and to retinal photoreceptor and pigmented epithelium cells. Consistent with molecular modeling predictions of calcium binding, CIB2 significantly decreased the ATP-induced calcium responses in heterologous cells, whereas mutations in deafness DFNB48 altered CIB2 effects on calcium responses. Furthermore, in zebrafish and Drosophila melanogaster, CIB2 is essential for the function and proper development of hair cells and retinal photoreceptor cells. We also show that CIB2 is a new member of the vertebrate Usher interactome.
Figures


Comment in
-
Mutations in CIB2 calcium and integrin-binding protein disrupt auditory hair cell calcium homeostasis in Usher syndrome type 1J and non-syndromic deafness DFNB48.Clin Genet. 2013 Apr;83(4):317-8. doi: 10.1111/cge.12100. Clin Genet. 2013. PMID: 23331261 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahmad J, et al. DFNB48, a new nonsyndromic recessive deafness locus, maps to chromosome 15q23-q25.1. Hum Genet. 2005;116:407–12. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz JM, Rodelsperger C, Schuelke M, Seelow D. MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nature methods. 2010;7:575–6. - PubMed
-
- Gentry HR, et al. Structural and biochemical characterization of CIB1 delineates a new family of EF-hand-containing proteins. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:8407–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- R01 DC009645/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DC011651/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092544/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC011651/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC012564/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC003594/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DC000039-15/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC011803/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG065403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC008861/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC011748/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DC011803/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DC000039/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DC009287/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC03594/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DC000039/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014648/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

