Classification of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody vasculitides: the role of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody specificity for myeloperoxidase or proteinase 3 in disease recognition and prognosis
- PMID: 23023777
- PMCID: PMC3462364
- DOI: 10.1002/art.34562
Classification of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody vasculitides: the role of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody specificity for myeloperoxidase or proteinase 3 in disease recognition and prognosis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the usefulness of 3 currently used classification systems in predicting the outcomes of treatment resistance, disease relapse, end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and death in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV).
Methods: Three classification systems were applied to 502 patients with biopsy-proven AAV: 1) the Chapel Hill Consensus Conference (CHCC) definition with categories for granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) (Wegener's), microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), and kidney-limited disease; 2) the European Medicines Agency (EMA) system with categories for GPA and MPA; and 3) classification based on ANCA with specificity for myeloperoxidase (MPO ANCA) versus ANCA with specificity for proteinase 3 (PR3 ANCA). Outcomes included treatment resistance, relapse, ESRD, and death. Proportional hazards models were compared between systems using an information-theoretic approach to rank models by predictive fit. Hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) and P values are reported.
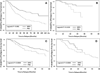
Results: ANCA specificity was predictive of relapse, with PR3 ANCA-positive patients almost twice as likely to relapse as those with MPO ANCA (HR 1.89 [95% CI 1.33-2.69], P = 0.0004), and ANCA specificity had the best predictive model fit (model rank 1) compared to the CHCC and EMA systems. The CHCC and EMA systems did not predict relapse. By ANCA specificity, categories of GPA, MPA, and kidney-limited disease did not distinguish differences in probability of relapse-free survival. None of the systems predicted treatment resistance, ESRD, or death.
Conclusion: ANCA specificity independently predicts relapse among patients with AAV with renal disease. Classification and diagnostic systems that incorporate ANCA specificity, such as PR3 ANCA-positive MPA and MPO ANCA-positive MPA, provide a more useful tool than the clinical pathologic category alone for predicting relapse.
Copyright © 2012 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies: an unbiased and efficient tool to classify renal vasculitis? Comment on the article by Lionaki et al.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 May;65(5):1405-6. doi: 10.1002/art.37892. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23400524 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, Bacon PA, Churg J, Gross WL, Hagen EC, Hoffman GS, Hunder GG, Kallenberg CG. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:187–192. - PubMed
-
- Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Koldingsnes W, Mahr A, Segelmark M, Cohen-Tervaert JW, Scott D. Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:222–227. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fries JF, Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, Arend WP, Calabrese LH, Fauci AS, Leavitt RY, Lie JT, Lightfoot RW., Jr The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of vasculitis. Summary. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1135–1136. - PubMed
-
- Falk RJ, Gross WL, Guillevin L, Hoffman GS, Jayne DR, Jennette JC, Kallenberg CG, Luqmani R, Mahr AD, Matteson EL, Merkel PA, Specks U, Watts RA. Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener's): An alternative name for Wegener's Granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:863–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

