Unusual C=C bond isomerization of an α,β-unsaturated γ-butyrolactone catalysed by flavoproteins from the old yellow enzyme family
- PMID: 23024004
- PMCID: PMC3533789
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201200475
Unusual C=C bond isomerization of an α,β-unsaturated γ-butyrolactone catalysed by flavoproteins from the old yellow enzyme family
Abstract
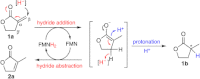
An unexpected, redox-neutral C=C bond isomerization of a γ-butyrolactone bearing an exo-methylene unit to the thermodynamically more favoured endo isomer (k(cat) =0.076 s(-1) ) catalysed by flavoproteins from the Old Yellow Enzyme family was discovered. Theoretical calculations and kinetic data support a mechanism through which the isomerization proceeds through FMN-mediated hydride addition onto exo-Cβ, followed by hydride abstraction from endo-Cβ', which is in line with the well-established C=C bond bioreduction of OYEs. This new isomerase activity enriches the catalytic versatility of ene-reductases.
Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



References
-
- Brenna E, Fuganti C, Serra S. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2003;14:1–42.
-
- Serra S, Fuganti C, Brenna E. Trends Biotechnol. 2005;23:193–198. - PubMed
-
- Mase N, Inoue A, Nishio M, Takabe K. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009;19:3955–3958. - PubMed
-
- Pandey RK, Upadhyay RK, Shinde SS, Kumar P. Synth. Commun. 2004;34:2323–2329.
-
- Nishikori H, Ito K, Katsuki T. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 1998;9:1165–1170.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

