Differential diagnosis of lupus and primary membranous nephropathies by IgG subclass analysis
- PMID: 23024158
- PMCID: PMC3513749
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.04800511
Differential diagnosis of lupus and primary membranous nephropathies by IgG subclass analysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Previous studies showed that the accuracy of IgG subclasses (ISs) in differentiating membranous lupus nephritis (MLN) from primary membranous nephropathy (PMN) is <80%. This study hypothesized that diagnostic accuracy of ISs would be increased if renal compartment measurements and decision tree analysis are applied.
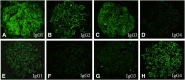
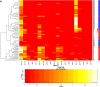
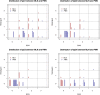
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Renal biopsy specimens from 41 patients with MLN and 59 patients with PMN between October 2004 and March 2010 were examined, and immunofluorescence staining against IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 as well as C3, C1q, and C4 was evaluated in five different renal compartments (glomerular capillary walls, mesangium, tubules, interstitium, and blood vessels). From IS data, a decision tree to differentiate MLN from PMN was produced (IS decision tree) and its accuracy was compared with that of previous studies. Diagnostic accuracy of the IS decision tree was also compared with that of the complement decision tree as a reference.
Results: The demographic information and patterns of IS deposition were similar to those of previous studies. The IS decision tree had, as decision markers, IgG1 in the mesangium and IgG2 and IgG4 along the glomerular capillary wall. The IS decision tree showed higher accuracy (88%) than that of previous studies (<80%) and also that of the complement decision tree (81%).
Conclusions: Accuracy of ISs was increased due to the study methods, but the same methodology was less effective using complement measurements. Appropriate data analysis may enhance diagnostic value, but the analysis alone cannot achieve the ideal diagnostic value.
Figures


References
-
- Flanagan JG, Rabbitts TH: Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature 300: 709–713, 1982 - PubMed
-
- Jefferis R: Polyclonal and monoclonal antibody reagents specific for IgG subclasses. Monogr Allergy 19: 71–85, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Hammarström L, Smith CI: IgG subclasses in bacterial infections. Monogr Allergy 19: 122–133, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Shakib F, Stanworth DR: Human IgG subclasses in health and disease. (A review). Part II. Ric Clin Lab 10: 561–580, 1980 - PubMed
-
- Shakib F, Stanworth DR: Human IgG subclasses in health and disease. (A review). Part I. Ric Clin Lab 10: 463–479, 1980 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

