Role of substance P in renal injury during DOCA-salt hypertension
- PMID: 23024265
- PMCID: PMC3512068
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2012-1284
Role of substance P in renal injury during DOCA-salt hypertension
Abstract
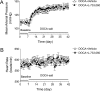
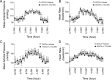
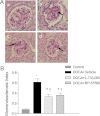
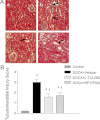
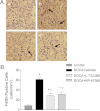
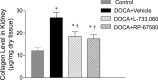
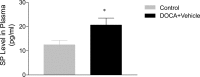
Substance P (SP), a neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) agonist, is mainly produced and stored in primary sensory nerves and, upon its release, participates in cardiovascular and renal functional regulation. This study tests the hypothesis that activation of the NK-1Rs by SP occurs during hypertension induced by deoxycorticosterone (DOCA)-salt treatment, which contributes to renal injury in this model. C57BL/6 mice were subjected to uninephrectomy and DOCA-salt treatment in the presence or absence of administration of selective NK-1 antagonists, L-733,060 (20 mg/kg·d, ip) or RP-67580 (8 mg/kg·d, ip). Five weeks after the treatment, mean arterial pressure determined by the telemetry system increased in DOCA-salt mice but without difference between NK-1R antagonist-treated or NK-1R antagonist-untreated DOCA-salt groups. Plasma SP levels were increased in DOCA-salt compared with control mice (P < 0.05). Renal hypertrophy and increased urinary 8-isoprostane and albumin excretion were observed in DOCA-salt compared with control mice (P < 0.05). Periodic acid-Schiff and Masson's trichrome staining showed more severe glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial injury in the renal cortex in DOCA-salt compared with control mice, respectively (P < 0.05). Hydroxyproline assay and F4/80-staining showed that renal collagen levels and interstitial monocyte/macrophage infiltration were greater in DOCA-salt compared with control mice, respectively (P < 0.05). Blockade of the NK-1R with L-733,060 or RP-67580 in DOCA-salt mice suppressed increments in urinary 8-isoprostane and albumin excretion, interstitial monocyte/macrophage infiltration, and glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial injury and fibrosis (P < 0.05). Thus, our data show that blockade of the NK-1Rs alleviates renal functional and tissue injury in the absence of alteration in blood pressure in DOCA-salt-hypertensive mice. The results suggest that elevated SP levels during DOCA-salt hypertension play a significant role contributing to renal damage possibly via enhancing oxidative stress and macrophage infiltration of the kidney.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/C-C chemokine receptor 2 signaling pathway in transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 ablation-induced renal injury in salt-sensitive hypertension.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Sep;240(9):1223-34. doi: 10.1177/1535370214565970. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25585624 Free PMC article.
-
Aggravated renal inflammatory responses in TRPV1 gene knockout mice subjected to DOCA-salt hypertension.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 Dec;297(6):F1550-9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00012.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19794112 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide attenuates renal damage by limiting inflammatory responses in DOCA-salt hypertension.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Dec;89(Pt A):107035. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107035. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33045566
-
[Role of chemokine receptor 2 in renal damage induced by deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertension].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2013 Feb;35(1):29-35. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2013.01.006. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 23469787 Chinese.
-
The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of primary hypertension.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Dec;27 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):iv2-5. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs421. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 23036901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular metabolism of substance P produces neurokinin-1 receptor peptide agonists with diminished cyclic AMP signaling.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Jul 1;327(1):C151-C167. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00103.2024. Epub 2024 May 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38798270 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/C-C chemokine receptor 2 signaling pathway in transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 ablation-induced renal injury in salt-sensitive hypertension.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Sep;240(9):1223-34. doi: 10.1177/1535370214565970. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25585624 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of mineralocorticoid treatment in mice with collecting duct-specific knockout of endothelin-1.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Dec 15;309(12):F1026-34. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00220.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26400543 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Substance P in Pulmonary Clearance of Bacteria in Comparative Injury Models.Am J Pathol. 2016 Dec;186(12):3236-3245. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.08.014. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27876152 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Deficiency Improves Endothelial Function and Cardiovascular Injury in Deoxycorticosterone Acetate/Salt-Hypertensive Mice.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Feb 28;2020:3921074. doi: 10.1155/2020/3921074. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32190663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rostand SG, Kirk KA, Rutsky EA, Pate BA. 1982. Racial differences in incidences of treatment for end stage renal disease. N Engl J Med 306:1276–1279 - PubMed
-
- Vernerová Z, Kujal P, Kramer HJ, Bäcker A, Cervenka L, Vanecková I. 2009. End-organ damage in hypertensive transgenic Ren-2 rats: influence of early and late endothelin receptor blockade. Physiol Res 58:S69–S78 - PubMed
-
- Wimalawansa SJ. 1996. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and its receptors: molecular genetics, physiology, pathophysiolgy, and therapeutic potentials. Endocr Rev 17:533–585 - PubMed
-
- Kopp UC, Cicha MZ, Smith LA. 2003. Dietary sodium loading increases arterial pressure in afferent renal-denervated rats. Hypertension 42:968–973 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

