Surfactant phospholipid metabolism
- PMID: 23026158
- PMCID: PMC3562414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.09.010
Surfactant phospholipid metabolism
Abstract
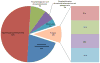
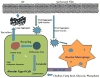
Pulmonary surfactant is essential for life and is composed of a complex lipoprotein-like mixture that lines the inner surface of the lung to prevent alveolar collapse at the end of expiration. The molecular composition of surfactant depends on highly integrated and regulated processes involving its biosynthesis, remodeling, degradation, and intracellular trafficking. Despite its multicomponent composition, the study of surfactant phospholipid metabolism has focused on two predominant components, disaturated phosphatidylcholine that confers surface-tension lowering activities, and phosphatidylglycerol, recently implicated in innate immune defense. Future studies providing a better understanding of the molecular control and physiological relevance of minor surfactant lipid components are needed. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled Phospholipids and Phospholipid Metabolism.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Veldhuizen R, Possmayer F. Phospholipid metabolism in lung surfactant. Subcell Biochem. 2004;37:359–88. - PubMed
-
- Lynch RG. Surfactant and RDS in premature infants. FASEB J. 2004;18(13):1624. - PubMed
-
- Anzueto A, et al. Aerosolized surfactant in adults with sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Exosurf Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Sepsis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(22):1417–21. - PubMed
-
- Wright JR, Clements JA. Metabolism and turnover of lung surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987;136(2):426–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

