The WNK/SPAK and IRBIT/PP1 pathways in epithelial fluid and electrolyte transport
- PMID: 23026752
- PMCID: PMC3686318
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00028.2012
The WNK/SPAK and IRBIT/PP1 pathways in epithelial fluid and electrolyte transport
Abstract
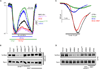
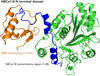
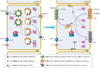
Fluid and electrolyte homeostasis is a fundamental physiological function required for survival and is associated with a plethora of diseases when aberrant. Systemic fluid and electrolyte composition is regulated by the kidney, and all secretory epithelia generate biological fluids with defined electrolyte composition by vectorial transport of ions and the obligatory water. A major regulatory pathway that immerged in the last several years is regulation of ion transporters by the WNK/SPAK kinases and IRBIT/PP1 pathways. The IRBIT/PP1 pathway functions to reverse the effects of the WNK/SPAK kinases pathway, as was demonstrated for NBCe1-B and CFTR. Since many transporters involved in fluid and electrolyte homeostasis are affected by PP1 and/or calcineurin, it is possible that WNK/SPAK and IRBIT/PP1 form a common regulatory pathway to tune the activity of fluid and electrolyte transport in response to physiological demands.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Ando H, Mizutani A, Kiefer H, Tsuzurugi D, Michikawa T, Mikoshiba K. IRBIT suppresses IP3 receptor activity by competing with IP3 for the common binding site on the IP3 receptor. Mol Cell. 2006;22:795–806. - PubMed
-
- Ando H, Mizutani A, Matsu-ura T, Mikoshiba K. IRBIT, a novel inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptor-binding protein, is released from the IP3 receptor upon IP3 binding to the receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:10602–10612. - PubMed
-
- Ando H, Mizutani A, Mikoshiba K. An IRBIT homologue lacks binding activity to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor due to the unique N-terminal appendage. J Neurochem. 2009;109:539–550. - PubMed
-
- Beneken J, Tu JC, Xiao B, Nuriya M, Yuan JP, Worley PF, Leahy DJ. Structure of the Homer EVH1 domain-peptide complex reveals a new twist in polyproline recognition. Neuron. 2000;26:143–154. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron MJ, Frenette-Cotton R, Carpentier GA, Simard MG, Caron L, Isenring P. Phosphoregulation of K+-Cl− cotransporter 4 during changes in intracellular Cl− and cell volume. J Cell Physiol. 2009;219:787–796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

