Unusual localization and translocation of TRPV4 protein in cultured ventricular myocytes of the neonatal rat
- PMID: 23027348
- PMCID: PMC3493978
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2012.e32
Unusual localization and translocation of TRPV4 protein in cultured ventricular myocytes of the neonatal rat
Abstract
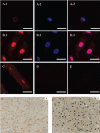
TRPV4 protein forms a Ca2+-permeable channel that is sensitive to osmotic and mechanical stimuli and responds to warm temperatures, and expresses widely in various kinds of tissues. As for cardiac myocytes, TRPV4 has been detected only at the mRNA level and there were few reports about subcellular localization of the protein. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the expression profile of TRPV4 protein in cultured neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. Using Western blots, immunofluorescence, confocal microscopy and immuno-electron microscopy, we have shown that TRPV4 protein was predominantly located in the nucleus of cultured neonatal myocytes. Furthermore, cardiac myocytes responded to hypotonic stimulation by translocating TRPV4 protein out of the nucleus. The significance and mechanism concerning the unusual distribution and translocation of TRPV4 protein in cardiac myocytes remain to be clarified.
Figures


References
-
- Montell C, Rubin GM. Molecular characterization of the drosophila trp locus: A putative integral membrane protein required for phototransduction. Neuron. 1989;2:1313–23. - PubMed
-
- Koulen P, Cai Y, Geng L, Maeda Y, Nishimura S, Witzgall R, et al. Polycystin-2 is an intracellular calcium release channel. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:191–7. - PubMed
-
- Loot AE, Popp R, Fisslthaler B, Vriens J, Nilius B, Fleming I. Role of cytochrome P450-dependent transient receptor potential V4 activation in flow-induced vasodi-latation. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;80:445–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

