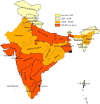
Estimate of HIV prevalence and number of people living with HIV in India 2008-2009
- PMID: 23028110
- PMCID: PMC3488742
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-000926
Estimate of HIV prevalence and number of people living with HIV in India 2008-2009
Abstract
Objectives: To update the estimation of the adult HIV prevalence and number of people living with HIV (PLHIV) in India for the year 2008-2009 with the combination of improved data and methods.
Design: Based on HIV sentinel surveillance (HSS) data and a set of epidemiological assumptions, estimates of HIV prevalence and burden in India have been derived.
Setting: HSS sites spread over all the States of India.
Participants: Secondary data from HSS sites which include attendees of antenatal clinics and sites under targeted interventions of high-risk groups, namely, female sex workers (FSW), intravenous drug users (IDU) and men having sex with men (MSM).
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Estimates of adult HIV prevalence and PLHIV in India and its states.
Results: The adult HIV prevalence in India has declined to an estimated 0.31% (0.25-0.39%) in 2009 against 0.36% (0.29-0.45%) in 2006. Among the high prevalence states, the HIV prevalence has declined in Tamil Nadu to 0.33% in 2009 and other states show either a plateau or a slightly declining trend over the time period 2006-2009. There are states in the low prevalence states where the adult HIV prevalence has risen over the last 4 years. The estimated number of PLHIV in India is 2.4 million (1.93-3.04 million) in 2009. Of which, 39% are women, children under 15 years of age account for 4.4% of all infections, while people aged 15-49 years account for 82.4% of all infections.
Conclusions: The estimated adult prevalence has declined in few states, a plateau or a slightly declining trend over the time. In future, efforts may be made to examine the implications of the emerging trend of the HIV prevalence on the recent infections in the study population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improved estimates of India's HIV burden in 2006.Indian J Med Res. 2009 Jan;129(1):50-8. Indian J Med Res. 2009. PMID: 19287057
-
Is the HIV burden in India being overestimated?BMC Public Health. 2006 Dec 20;6:308. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-6-308. BMC Public Health. 2006. PMID: 17181865 Free PMC article.
-
A population-based study of human immunodeficiency virus in south India reveals major differences from sentinel surveillance-based estimates.BMC Med. 2006 Dec 13;4:31. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-4-31. BMC Med. 2006. PMID: 17166257 Free PMC article.
-
HIV prevalence trend from HIV sentinel surveillance over a decade in India: An overview.Indian J Public Health. 2018 Apr-Jun;62(2):138-142. doi: 10.4103/ijph.IJPH_151_16. Indian J Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29923539 Review.
-
Rising HIV infection rates in Ho Chi Minh City herald emerging AIDS epidemic in Vietnam.AIDS. 1997 Sep;11 Suppl 1:S5-13. AIDS. 1997. PMID: 9376101 Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity among clients of female sex workers in India: comparing risk profiles and intervention impact by site of solicitation. implications for the vulnerability of less visible female sex workers.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 2;8(9):e73470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073470. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023877 Free PMC article.
-
Findings from the 2017 HIV estimation round & trend analysis of key indicators 2010-2017: Evidence for prioritising HIV/AIDS programme in India.Indian J Med Res. 2020 Jun;151(6):562-570. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1619_19. Indian J Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32719229 Free PMC article.
-
Vulnerability of Bangladeshi street-children to HIV/AIDS: a qualitative study.BMC Public Health. 2014 Nov 6;14:1151. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-1151. BMC Public Health. 2014. PMID: 25373415 Free PMC article.
-
A clinico-epidemiological study, assessing possible predictors of mortality and health-related quality of life for people living with visceral leishmaniasis - human immune virus (VL-HIV) co-infection in a high burden kala-azar endemic state of India: a descriptive cross-sectional study.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):887. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10768-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40604450 Free PMC article.
-
How varying CD4 criteria for treatment initiation was associated with mortality of HIV-patients? A retrospective analysis of electronic health records from Andhra Pradesh, India.J Glob Health. 2020 Jun;10(1):010408. doi: 10.7189/jogh.10.010408. J Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32257156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institute of Health & Family Welfare . Country Report on Annual HIV Sentinel Surveillance, 2006, New Delhi: National AIDS Control Organization (NACO), Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, 2007
-
- International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) and Macro International India, IIPS, Mumbai: National Family Health Survey, 2005–2006 (NFHS-3), 2007
-
- Pandey A, Reddy DCS, Ghys P, et al. Improved estimate of India's HIV burden in 2006. Indian J Med Res 2009;129:50–8 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases