Radiation dose reduction in CT-guided sacroiliac joint injections to levels of pulsed fluoroscopy: a comparative study with technical considerations
- PMID: 23028237
- PMCID: PMC3442745
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S34429
Radiation dose reduction in CT-guided sacroiliac joint injections to levels of pulsed fluoroscopy: a comparative study with technical considerations
Abstract
Background: The sacroiliac (SI) joint is frequently the primary source of low back pain. Over the past decades, a number of different SI injection techniques have been used in its diagnosis and therapy. Despite the concerns regarding exposure to radiation, image-guided injection techniques are the preferred method to achieve safe and precise intra-articular needle placement. The following study presents a comparison of radiation doses, calculated for fluoroscopy and CT-guided SI joint injections in standard and low-dose protocol and presents the technical possibility of CT-guidance with maximum radiation dose reduction to levels of fluoroscopic-guidance for a precise intra-articular injection technique.
Objective: To evaluate the possibility of dose reduction in CT-guided sacroiliac joint injections to pulsed-fluoroscopy-guidance levels and to compare the doses of pulsed-fluoroscopy-, CT-guidance, and low-dose CT-guidance for intra-articular SI joint injections.
Study design: Comparative study with technical considerations.
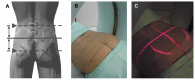
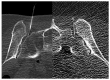
Methods: A total of 30 CT-guided intra-articular SI joint injections were performed in January 2012 in a developed low-dose mode and the radiation doses were calculated. They were compared to 30 pulsed-fluoroscopy-guided SI joint injections, which were performed in the month before, and to five injections, performed in standard CT-guided biopsy mode for spinal interventions. The statistical significance was calculated with the SPSS software using the Mann-Whitney U-Test. Technical details and anatomical considerations were provided.
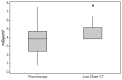
Results: A significant dose reduction of average 94.01% was achieved using the low-dose protocol for CT-guided SI joint injections. The radiation dose could be approximated to pulsed-fluoroscopy- guidance levels.
Conclusion: Radiation dose of CT-guided SI joint injections can be decreased to levels of pulsed fluoroscopy with a precise intra-articular needle placement using the low-dose protocol. The technique is simple to perform, fast, and reproducible.
Keywords: computed tomography; guided injections; low back pain; low-dose protocol; radiation dose; sacroiliac joint injection; sacroiliac joint pain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Cadaveric Study Assessing the Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Sacroiliac Joint Injections.PM R. 2016 Dec;8(12):1168-1172. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 May 10. PM R. 2016. PMID: 27178376
-
Sacroiliac joint syndrome after lumbosacral fusion.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020 Oct;106(6):1233-1238. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32900669
-
Image Guidance Technologies for Interventional Pain Procedures: Ultrasound, Fluoroscopy, and CT.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018 Jan 26;22(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s11916-018-0660-1. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374352 Review.
-
Computerized tomographic localization of clinically-guided sacroiliac joint injections.Clin J Pain. 2000 Mar;16(1):18-21. doi: 10.1097/00002508-200003000-00004. Clin J Pain. 2000. PMID: 10741814 Clinical Trial.
-
Review of Sacroiliac Joint Injection Techniques.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2022 May;26(5):385-390. doi: 10.1007/s11916-022-01037-7. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2022. PMID: 35239155 Review.
Cited by
-
CT-guided corticosteroid injection of the sacroiliac joints: quality assurance and standardized prospective evaluation of long-term effectiveness over six months.Clin Rheumatol. 2015 Jun;34(6):1079-84. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2937-7. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Clin Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25896531
-
FEASIBILITY OF COLOUR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND FOR DETECTION OF INTRAARTICULAR SACROILIAC JOINT INJECTION: A CASE SERIES.Ulster Med J. 2020 Jan;89(1):42-43. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Ulster Med J. 2020. PMID: 32218631 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Computed Tomography of the Spine : Systematic Review on Acquisition and Reconstruction Techniques to Reduce Radiation Dose.Clin Neuroradiol. 2023 Jun;33(2):271-291. doi: 10.1007/s00062-022-01227-1. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Clin Neuroradiol. 2023. PMID: 36416936 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics, treatment and outcomes of acute postpartum inflammatory sacroiliitis: a retrospective study.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022 Dec;306(6):2187-2195. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06534-z. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 35396619
-
CT-guided joint cavity release for postpartum sacroiliac joint pain management: an evaluation of its efficacy, safety, and clinical outcomes.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 26;11:1417673. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1417673. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39399111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hansen HC, McKenzie-Brown AM, Cohen SP, Swicegood JR, Colson JD, Manchikanti L. Sacroiliac joint interventions: a systematic review. Pain Physician. 2007;10(1):165–184. - PubMed
-
- Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, et al. The false-positive rate of uncontrolled diagnostic blocks of the lumbar zygapophysial joints. Pain. 1994;58:195–200. - PubMed
-
- van der Wurff P, Meyne W, Hagmeijer RH. Clinical tests of the sacroiliac joint. Manual Ther. 2000;5(2):89–96. - PubMed
-
- Riddle DL, Freburger JK. Evaluation of the presence of sacroiliac joint dysfunction using a combination of tests: a multicenter intertester reliability study. Phys Ther. 2002;82:772–781. - PubMed
-
- Dussault RG, Kaplan PA, Anderson MW. Fluoroscopy-guided sacroiliac joint injections. Radiology. 2000;214(1):273–277. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

