Marburg virus VP35 can both fully coat the backbone and cap the ends of dsRNA for interferon antagonism
- PMID: 23028316
- PMCID: PMC3441732
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002916
Marburg virus VP35 can both fully coat the backbone and cap the ends of dsRNA for interferon antagonism
Abstract
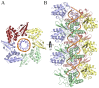
Filoviruses, including Marburg virus (MARV) and Ebola virus (EBOV), cause fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and non-human primates. All filoviruses encode a unique multi-functional protein termed VP35. The C-terminal double-stranded (ds)RNA-binding domain (RBD) of VP35 has been implicated in interferon antagonism and immune evasion. Crystal structures of the VP35 RBD from two ebolaviruses have previously demonstrated that the viral protein caps the ends of dsRNA. However, it is not yet understood how the expanses of dsRNA backbone, between the ends, are masked from immune surveillance during filovirus infection. Here, we report the crystal structure of MARV VP35 RBD bound to dsRNA. In the crystal structure, molecules of dsRNA stack end-to-end to form a pseudo-continuous oligonucleotide. This oligonucleotide is continuously and completely coated along its sugar-phosphate backbone by the MARV VP35 RBD. Analysis of dsRNA binding by dot-blot and isothermal titration calorimetry reveals that multiple copies of MARV VP35 RBD can indeed bind the dsRNA sugar-phosphate backbone in a cooperative manner in solution. Further, MARV VP35 RBD can also cap the ends of the dsRNA in solution, although this arrangement was not captured in crystals. Together, these studies suggest that MARV VP35 can both coat the backbone and cap the ends, and that for MARV, coating of the dsRNA backbone may be an essential mechanism by which dsRNA is masked from backbone-sensing immune surveillance molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Martini GA, Siegert R (1971) Marburg Virus Disease. New York: Springer.
-
- Sanchez A, Geisbert TW, Feldmann H (2007) Filoviridae: Marburg and Ebola viruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA et al..., editors. Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. pp. 1409–1448.
-
- World Health Organization (2005) Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever. World Health Organization.
-
- Baize S, Leroy EM, Georges-Courbot MC, Capron M, Lansoud-Soukate J, et al. (1999) Defective humoral responses and extensive intravascular apoptosis are associated with fatal outcome in Ebola virus-infected patients. Nat Med 5: 423–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

