Global assessment of genomic regions required for growth in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 23028335
- PMCID: PMC3460630
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002946
Global assessment of genomic regions required for growth in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Erratum in
- PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(7). doi:10.1371/annotation/4669e9e7-fd12-4a01-be2a-617b956ec0bb
Abstract
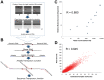
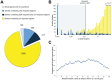
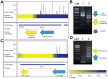
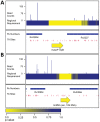
Identifying genomic elements required for viability is central to our understanding of the basic physiology of bacterial pathogens. Recently, the combination of high-density mutagenesis and deep sequencing has allowed for the identification of required and conditionally required genes in many bacteria. Genes, however, make up only a part of the complex genomes of important bacterial pathogens. Here, we use an unbiased analysis to comprehensively identify genomic regions, including genes, domains, and intergenic elements, required for the optimal growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a major global health pathogen. We found that several proteins jointly contain both domains required for optimal growth and domains that are dispensable. In addition, many non-coding regions, including regulatory elements and non-coding RNAs, are critical for mycobacterial growth. Our analysis shows that the genetic requirements for growth are more complex than can be appreciated using gene-centric analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Gawronski JD, Wong SMS, Giannoukos G, Ward DV, Akerley BJ (2009) Tracking insertion mutants within libraries by deep sequencing and a genome-wide screen for Haemophilus genes required in the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 16422–16427 doi:10.1073/pnas.0906627106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goodman AL, Mcnulty NP, Zhao Y, Leip D, Mitra RD, et al. (2009) Identifying Genetic Determinants Needed to Establish a Human Gut Symbiont in Its Habitat. Cell Host Microbe 6: 279–289 doi:10.1016/j.chom.2009.08.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Griffin JE, Gawronski JD, DeJesus MA, Ioerger TR, Akerley BJ, et al. (2011) High-resolution phenotypic profiling defines genes essential for mycobacterial growth and cholesterol catabolism. PLoS Pathog 7: e1002251 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002251. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Langridge GC, Phan M-D, Turner DJ, Perkins TT, Parts L, et al. (2009) Simultaneous assay of every Salmonella Typhi gene using one million transposon mutants. Genome Res 19: 2308–2316 doi:10.1101/gr.097097.109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Opijnen T, Bodi KL, Camilli A (2009) Tn-seq: high-throughput parallel sequencing for fitness and genetic interaction studies in microorganisms. Nat Methods 6: 767–772 doi:10.1038/nmeth.1377. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

