The Therapeutic Potential for PI3K Inhibitors in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases
- PMID: 23028409
- PMCID: PMC3460535
- DOI: 10.2174/1874312901206010245
The Therapeutic Potential for PI3K Inhibitors in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases
Abstract
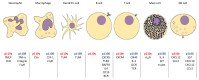
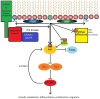
The class 1 PI3Ks are lipid kinases with key roles in cell surface receptor-triggered signal transduction pathways. Two isoforms of the catalytic subunits, p110γ and p110δ, are enriched in leucocytes in which they promote activation, cellular growth, proliferation, differentiation and survival through the generation of the second messenger PIP3. Genetic inactivation or pharmaceutical inhibition of these PI3K isoforms in mice result in impaired immune responses and reduced susceptibility to autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. We review the PI3K signal transduction pathways and the effects of inhibition of p110γ and/or p110δ on innate and adaptive immunity. Focusing on rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus we discuss the preclinical evidence and prospects for small molecule inhibitors of p110γ and/or p110δ in autoimmune disease.
Keywords: PI3K inhibitors; PI3K.; autoimmunity; humoral immune; pleckstrin homology; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
References
-
- Nathan C, Ding A. Nonresolving inflammation. Cell. 2010;140(6 ): 871–82. - PubMed
-
- Rai E, Wakeland EK. Genetic predisposition to autoimmunity-- what have we learned? Semin Immunol. 2011;23(2 ):67–83. - PubMed
-
- Rommel C, Camps M, Ji H. PI3K delta and PI3K gamma: partners in crime in inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and beyond? Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(3 ):191–201. - PubMed
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M, Bilanges B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(5 ):329–41. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
