An integrated pipeline for de novo assembly of microbial genomes
- PMID: 23028432
- PMCID: PMC3441570
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042304
An integrated pipeline for de novo assembly of microbial genomes
Abstract
Remarkable advances in DNA sequencing technology have created a need for de novo genome assembly methods tailored to work with the new sequencing data types. Many such methods have been published in recent years, but assembling raw sequence data to obtain a draft genome has remained a complex, multi-step process, involving several stages of sequence data cleaning, error correction, assembly, and quality control. Successful application of these steps usually requires intimate knowledge of a diverse set of algorithms and software. We present an assembly pipeline called A5 (Andrew And Aaron's Awesome Assembly pipeline) that simplifies the entire genome assembly process by automating these stages, by integrating several previously published algorithms with new algorithms for quality control and automated assembly parameter selection. We demonstrate that A5 can produce assemblies of quality comparable to a leading assembly algorithm, SOAPdenovo, without any prior knowledge of the particular genome being assembled and without the extensive parameter tuning required by the other assembly algorithm. In particular, the assemblies produced by A5 exhibit 50% or more reduction in broken protein coding sequences relative to SOAPdenovo assemblies. The A5 pipeline can also assemble Illumina sequence data from libraries constructed by the Nextera (transposon-catalyzed) protocol, which have markedly different characteristics to mechanically sheared libraries. Finally, A5 has modest compute requirements, and can assemble a typical bacterial genome on current desktop or laptop computer hardware in under two hours, depending on depth of coverage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
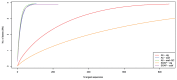
 largest sequences. Assemblies generated from SOAPdenovo and A5 are labelled with “SOAP” and “A5”, respectively. “scaf” indicates an assembly that has been scaffolded, while “ctg” indicates no scaffolding. For A5, assembly “scaf-QC” has been broken using the A5QC algorithm and rescaffolded using SSPACE. A perfect assembly would have exactly the number of sequences as the organism has replicons (5 in this case), and the curve would be in the extreme upper left corner.
largest sequences. Assemblies generated from SOAPdenovo and A5 are labelled with “SOAP” and “A5”, respectively. “scaf” indicates an assembly that has been scaffolded, while “ctg” indicates no scaffolding. For A5, assembly “scaf-QC” has been broken using the A5QC algorithm and rescaffolded using SSPACE. A perfect assembly would have exactly the number of sequences as the organism has replicons (5 in this case), and the curve would be in the extreme upper left corner.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

