Metformin prevents and reverses inflammation in a non-diabetic mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 23028442
- PMCID: PMC3445596
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043056
Metformin prevents and reverses inflammation in a non-diabetic mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
Background: Optimal treatment for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) has not yet been established, particularly for individuals without diabetes. We examined the effects of metformin, commonly used to treat patients with type 2 diabetes, on liver pathology in a non-diabetic NASH mouse model.
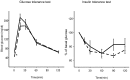
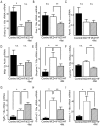
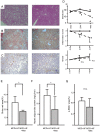
Methodology/principal findings: Eight-week-old C57BL/6 mice were fed a methionine- and choline-deficient plus high fat (MCD+HF) diet with or without 0.1% metformin for 8 weeks. Co-administration of metformin significantly decreased fasting plasma glucose levels, but did not affect glucose tolerance or peripheral insulin sensitivity. Metformin ameliorated MCD+HF diet-induced hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. Furthermore, metformin significantly reversed hepatic steatosis and inflammation when administered after the development of experimental NASH.
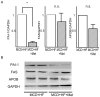
Conclusions/significance: These histological changes were accompanied by reduced hepatic triglyceride content, suppressed hepatic stellate cell activation, and the downregulation of genes involved in fatty acid metabolism, inflammation, and fibrogenesis. Metformin prevented and reversed steatosis and inflammation of NASH in an experimental non-diabetic model without affecting peripheral insulin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Marchesini G, Brizi M, Morselli-Labate AM, Bianchi G, Bugianesi E, et al. (1999) Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with insulin resistance. Am J Med 107: 450–455. - PubMed
-
- Ota T, Takamura T, Kurita S, Matsuzawa N, Kita Y, et al. (2007) Insulin resistance accelerates a dietary rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 132: 282–293. - PubMed
-
- Belfort R, Harrison SA, Brown K, Darland C, Finch J, et al. (2006) A placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 355: 2297–2307. - PubMed
-
- Aithal GP, Thomas JA, Kaye PV, Lawson A, Ryder SD, et al. (2008) Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 135: 1176–1184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

