Simple and highly discriminatory VNTR-based multiplex PCR for tracing sources of Aspergillus flavus isolates
- PMID: 23028503
- PMCID: PMC3444452
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044204
Simple and highly discriminatory VNTR-based multiplex PCR for tracing sources of Aspergillus flavus isolates
Abstract
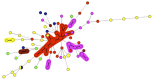
Aspergillus flavus is second only to A. fumigatus in causing invasive aspergillosis and it is the major agent responsible for fungal sinusitis, keratitis and endophthalmitis in many countries in the Middle East, Africa and Southeast Asia. Despite the growing challenge due to A. flavus, data on the molecular epidemiology of this fungus remain scarce. The objective of the present study was to develop a new typing method based on the detection of VNTR (Variable number tandem repeat) markers. Eight VNTR markers located on 6 different chromosomes (1, 2, 3, 5, 7 and 8) of A. flavus were selected, combined by pairs for multiplex amplifications and tested on 30 unrelated isolates and six reference strains. The Simpson index for individual markers ranged from 0.398 to 0.818. A combined loci index calculated with all the markers yielded an index of 0.998. The MLVA (Multiple Locus VNTR Analysis) technique proved to be specific and reproducible. In a second time, a total of 55 isolates from Chinese avian farms and from a Tunisian hospital have been evaluated. One major cluster of genotypes could be defined by using the graphing algorithm termed Minimum Spanning Tree. This cluster comprised most of the isolates collected in an avian farm in southern China. The MLVA technique should be considered as an excellent and cost-effective typing method that could be used in many laboratories without the need for sophisticated equipment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic structure of Aspergillus flavus populations in human and avian isolates.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013 Feb;32(2):277-82. doi: 10.1007/s10096-012-1740-5. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 22956010
-
Multiple-locus variable-number tandem repeat analysis for molecular typing of Aspergillus fumigatus.BMC Microbiol. 2010 Dec 8;10:315. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-315. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21143842 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Simple Universal Escherichia coli Genotyping Method Based on Multiple-Locus Variable-Number Tandem-Repeat Analysis Using Single-Tube Multiplex PCR and Standard Gel Electrophoresis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Mar 6;85(6):e02812-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02812-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30610078 Free PMC article.
-
A review molecular typing methods for Aspergillus flavus isolates.Mycopathologia. 2011 Aug;172(2):83-93. doi: 10.1007/s11046-011-9406-x. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Mycopathologia. 2011. PMID: 21369748 Review.
-
Multilocus variable number tandem repeat analysis for Salmonella enterica subspecies.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011 Apr;30(4):465-73. doi: 10.1007/s10096-010-1110-0. Epub 2010 Dec 11. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21153561 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of Aspergillus flavus populations associated with maize in Greece, Spain, and Serbia: Implications for aflatoxin biocontrol on a regional scale.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2024 Apr;16(2):e13249. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.13249. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38634243 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic structure of Aspergillus flavus populations in human and avian isolates.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013 Feb;32(2):277-82. doi: 10.1007/s10096-012-1740-5. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 22956010
-
Development of a Dot-Blot Assay for the Detection of Mould-Specific IgE in the Belgian Population.Mycopathologia. 2017 Apr;182(3-4):319-329. doi: 10.1007/s11046-016-0091-7. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Mycopathologia. 2017. PMID: 27878528
-
Multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis of clinical isolates of Aspergillus flavus from Iran reveals the first cases of Aspergillus minisclerotigenes associated with human infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Jul 1;14:358. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-358. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24986045 Free PMC article.
-
Multilocus variable-number-tandem-repeats analysis (MLVA) distinguishes a clonal complex of Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis strains isolated from recent outbreaks of bacterial wilt and canker in Belgium.BMC Microbiol. 2013 Jun 5;13:126. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-126. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23738754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denning DW (1998) Invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 26: 781–803. - PubMed
-
- Tell LA (2005) Aspergillosis in mammals and birds: impact on veterinary medicine. Med Mycol Suppl 1, S71–73. - PubMed
-
- Beernaert LA, Pasmans F, Van Waeyenberghe L, Haesebrouck F, Martel A (2010) Aspergillus infections in birds: a review. Avian Pathol 39: 325–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

