Anti-cancer activity of a novel small molecule compound that simultaneously activates p53 and inhibits NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 23028510
- PMCID: PMC3441512
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044259
Anti-cancer activity of a novel small molecule compound that simultaneously activates p53 and inhibits NF-κB signaling
Abstract
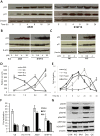
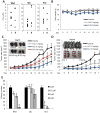
The p53 and NF-κB pathways play important roles in diverse cellular functions, including cell growth, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. Mutations that inactivate the p53 gene and constitutive NF-κB pathway activation are common occurrences in human cancers. Although many drugs are being developed that selectively activate p53 or inhibit NF-κB, there are few drug candidates that can do both. Simultaneous activation of p53 and inhibition of the NF-κB pathway is therefore a prime target for new cancer drug development. This study is the first report of a high-throughput approach with mass compounds that concurrently target both pathways. Using a cell-based screening assay and a library of 200,000 synthetic compounds, we identified 9 small molecules that simultaneously inhibit NF-κB and activate p53. One of these compounds, N-2, increased the expression of p53 target genes, including p21 and GADD45a. In addition, N-2 inhibited the transcriptional activity of NF-κB, concomitantly repressing interleukin-6 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) expression. When cell lines derived from a diverse range of cancers were treated in vitro with N-2, we observed increased cell death. N-2 also significantly inhibited allograft growth in murine models of melanoma and lung carcinoma. Our findings suggest that N-2 may act as a bivalent anti-cancer agent through simultaneous modulation of NF-κB and p53 activities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Double-edged swords as cancer therapeutics: novel, orally active, small molecules simultaneously inhibit p53-MDM2 interaction and the NF-κB pathway.J Med Chem. 2014 Feb 13;57(3):567-77. doi: 10.1021/jm401800k. Epub 2014 Jan 24. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24428757
-
Mutations of p53 and KRAS activate NF-κB to promote chemoresistance and tumorigenesis via dysregulation of cell cycle and suppression of apoptosis in lung cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2015 Feb 28;357(2):520-6. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.12.003. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25499080
-
Curaxins: anticancer compounds that simultaneously suppress NF-κB and activate p53 by targeting FACT.Sci Transl Med. 2011 Aug 10;3(95):95ra74. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002530. Sci Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21832239 Free PMC article.
-
P53 vs NF-κB: the role of nuclear factor-kappa B in the regulation of p53 activity and vice versa.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Nov;77(22):4449-4458. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03524-9. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32322927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic activation of NF-kappaB.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Jun;2(6):a000109. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000109. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20516126 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Akt/NF-κB/p53 Pathway and Apoptosis Inducing Potential of 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic Acid, Bis (2-Methyl Propyl) Ester Isolated from Onosma bracteata Wall. against Human Osteosarcoma (MG-63) Cells.Molecules. 2022 May 28;27(11):3478. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113478. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684419 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting nuclear factor-kappa B to overcome resistance to chemotherapy.Front Oncol. 2013 May 16;3:120. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00120. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23720710 Free PMC article.
-
The Melding of Drug Screening Platforms for Melanoma.Front Oncol. 2019 Jun 24;9:512. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00512. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31293965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The inflammatory cytokine TNFα cooperates with Ras in elevating metastasis and turns WT-Ras to a tumor-promoting entity in MCF-7 cells.BMC Cancer. 2014 Mar 6;14:158. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-158. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24598028 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of anticancer activity of quillaic acid derivatives: A cell cycle arrest and apoptosis inducer through NF-κB and MAPK pathways.Front Chem. 2022 Sep 7;10:951713. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.951713. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36157038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma HW, Narayanan R (1996) The NF-kappaB transcription factor in oncogenesis. Anticancer Res 16: 589–596. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D (1996) NF-kappa B: ten years after. Cell 87: 13–20. - PubMed
-
- Mayo MW, Baldwin AS (2000) The transcription factor NF-kappaB: control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1470: M55–62. - PubMed
-
- Gilmore TD, Herscovitch M (2006) Inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling: 785 and counting. Oncogene 25: 6887–6899. - PubMed
-
- Brown CJ, Lain S, Verma CS, Fersht AR, Lane DP (2009) Awakening guardian angels: drugging the p53 pathway. Nature Reviews Cancer 9: 862–873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

