Phyllostachys edulis compounds inhibit palmitic acid-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) production
- PMID: 23028772
- PMCID: PMC3445604
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045082
Phyllostachys edulis compounds inhibit palmitic acid-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) production
Abstract
Background: Phyllostachys edulis Carriere (Poaceae) is a bamboo species that is part of the traditional Chinese medicine pharmacopoeia. Compounds and extracts from this species have shown potential applications towards several diseases. One of many complications found in obesity and diabetes is the link between elevated circulatory free fatty acids (FFAs) and chronic inflammation. This study aims to present a possible application of P. edulis extract in relieving inflammation caused by FFAs. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1/CCL2) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine implicated in chronic inflammation. Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and activator protein 1 (AP-1) are transcription factors activated in response to inflammatory stimuli, and upregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines such as MCP-1. This study examines the effect of P. edulis extract on cellular production of MCP-1 and on the NF-κB and AP-1 pathways in response to treatment with palmitic acid (PA), a FFA.
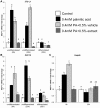
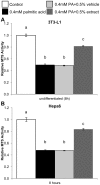
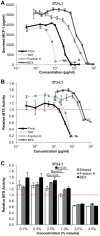
Methodology/principal findings: MCP-1 protein was measured by cytometric bead assay. NF-κB and AP-1 nuclear localization was detected by colorimetric DNA-binding ELISA. Relative MCP-1 mRNA was measured by real-time quantitative PCR. Murine cells were treated with PA to induce inflammation. PA increased expression of MCP-1 mRNA and protein, and increased nuclear localization of NF-κB and AP-1. Adding bamboo extract (BEX) inhibited the effects of PA, reduced MCP-1 production, and inhibited nuclear translocation of NF-κB and AP-1 subunits. Compounds isolated from BEX inhibited MCP-1 secretion with different potencies.
Conclusions/significance: PA induced MCP-1 production in murine adipose, muscle, and liver cells. BEX ameliorated PA-induced production of MCP-1 by inhibiting nuclear translocation of NF-κB and AP-1. Two O-methylated flavones were isolated from BEX with functional effects on MCP-1 production. These results may represent a possible therapeutic application of BEX and its compounds toward alleviating chronic inflammation caused by elevated circulatory FFAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Boden G (1998) Free fatty acids (FFA), a link between obesity and insulin resistance. Front Biosci 3: d169–175. - PubMed
-
- Boden G, She P, Mozzoli M, Cheung P, Gumireddy K, et al. (2005) Free fatty acids produce insulin resistance and activate the proinflammatory nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in rat liver. Diabetes 54: 3458–3465. - PubMed
-
- Conti P, DiGioacchino M (2001) MCP-1 and RANTES are mediators of acute and chronic inflammation. Allergy Asthma Proc 22: 133–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5P20RR016467-11/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR022762/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54RR022762/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AT003874/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007601/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- 8 G12 MD007601/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007584/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AT005139/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- 8 P20 GML 03466-11/PHS HHS/United States
- 5P20 MD000173-08/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR016467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD008149/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007601/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5 G12 RR003061/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003061/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD000173/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

