An inflammation loop orchestrated by S100A9 and calprotectin is critical for development of arthritis
- PMID: 23029038
- PMCID: PMC3445527
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045478
An inflammation loop orchestrated by S100A9 and calprotectin is critical for development of arthritis
Abstract
Objective: The S100A9 and S100A8 proteins are highly expressed by neutrophils and monocytes and are part of a group of damage-associated molecular pattern molecules that trigger inflammatory responses. Sera and synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) contain high concentrations of S100A8/A9 that correlate with disease activity.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the importance of S100A9 in RA by using neutralizing antibodies in a murine lipopolysaccharide-synchronized collagen-induced arthritis model. We also used an in vitro model of stimulation of human immune cells to decipher the role played by S100A9 in leukocyte migration and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion.
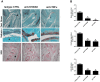
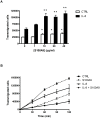
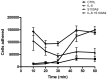
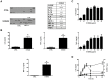
Results: Treatment with anti-S100A9 antibodies improved the clinical score by 50%, diminished immune cell infiltration, reduced inflammatory cytokines, both in serum and in the joints, and preserved bone/collagen integrity. Stimulation of neutrophils with S100A9 protein led to the enhancement of neutrophil transendothelial migration. S100A9 protein also induced the secretion by monocytes of proinflammatory cytokines like TNFα, IL-1β and IL-6, and of chemokines like MIP-1α and MCP-1.
Conclusion: The effects of anti-S100A9 treatment are likely direct consequences of inhibiting the S100A9-mediated promotion of neutrophil transmigration and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines from monocytes. Collectively, our results show that treatment with anti-S100A9 may inhibit amplification of the immune response and help preserve tissue integrity. Therefore, S100A9 is a promising potential therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis for which alternative therapeutic strategies are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
S100a8/a9 released by CD11b+Gr1+ neutrophils activates cardiac fibroblasts to initiate angiotensin II-Induced cardiac inflammation and injury.Hypertension. 2014 Jun;63(6):1241-50. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02843. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Hypertension. 2014. PMID: 24711518
-
S100A8/A9 increases the mobilization of pro-inflammatory Ly6Chigh monocytes to the synovium during experimental osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Sep 29;19(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1426-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28969686 Free PMC article.
-
Secretion of the Phosphorylated Form of S100A9 from Neutrophils Is Essential for the Proinflammatory Functions of Extracellular S100A8/A9.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 13;9:447. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00447. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29593718 Free PMC article.
-
S100 Calgranulins in inflammatory arthritis.Immunol Cell Biol. 2010 Jan;88(1):41-9. doi: 10.1038/icb.2009.88. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Immunol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19935766 Review.
-
S100A8 and S100A9 in inflammation and cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Nov 30;72(11):1622-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.05.017. Epub 2006 Jul 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16846592 Review.
Cited by
-
S100A9 Upregulation Contributes to Learning and Memory Impairments by Promoting Microglia M1 Polarization in Sepsis Survivor Mice.Inflammation. 2021 Feb;44(1):307-320. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01334-6. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 32918665
-
S100A9 plays a key role in Clostridium perfringens beta2 toxin-induced inflammatory damage in porcine IPEC-J2 intestinal epithelial cells.BMC Genomics. 2023 Jan 12;24(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09118-6. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36635624 Free PMC article.
-
S100A8/A9 in COVID-19 pathogenesis: Impact on clinical outcomes.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022 Feb;63:90-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2021.10.004. Epub 2021 Oct 17. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022. PMID: 34728150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S100A8/A9 (calprotectin) is critical for development of glomerulonephritis and promotes inflammatory leukocyte-renal cell interactions.Am J Pathol. 2015 May;185(5):1264-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.01.015. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25759267 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette smoke induction of S100A9 contributes to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):L1021-L1035. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00207.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32964723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marinova-Mutafchieva L, Williams RO, Mason LJ, Mauri C, Feldmann M, et al. (1997) Dynamics of proinflammatory cytokine expression in the joints of mice with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Clin Exp Immunol 107: 507–512. - PubMed
-
- Schrier DJ, Schimmer RC, Flory CM, Tung DK, Ward PA (1998) Role of chemokines and cytokines in a reactivation model of arthritis in rats induced by injection with streptococcal cell walls. J Leukoc Biol 63: 359–363. - PubMed
-
- Marie I, Guglielmino E (2010) [Non tuberculous anti-TNF associated opportunistic infections]. Rev Med Interne 31: 353–360. - PubMed
-
- Prinz JC (2011) Autoimmune-like syndromes during TNF blockade: does infection have a role? Nat Rev Rheumatol. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

