Overexpression of AtDREB1A causes a severe dwarf phenotype by decreasing endogenous gibberellin levels in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr]
- PMID: 23029105
- PMCID: PMC3445508
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045568
Overexpression of AtDREB1A causes a severe dwarf phenotype by decreasing endogenous gibberellin levels in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr]
Abstract
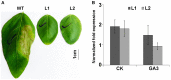
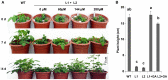
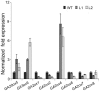
Gibberellic acids (GAs) are plant hormones that play fundamental roles in plant growth and developmental processes. Previous studies have demonstrated that three key enzymes of GA20ox, GA3ox, and GA2ox are involved in GA biosynthesis. In this study, the Arabidopsis DREB1A gene driven by the CaMV 35S promoter was introduced into soybean plants by Agrobacterium- mediated transformation. The results showed that the transgenic soybean plants exhibited a typical phenotype of GA-deficient mutants, such as severe dwarfism, small and dark-green leaves, and late flowering compared to those of the non-transgenic plants. The dwarfism phenotype was rescued by the application of exogenous GA(3) once a week for three weeks with the concentrations of 144 µM or three times in one week with the concentrations of 60 µM. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis revealed that the transcription levels of the GA synthase genes were higher in the transgenic soybean plants than those in controls, whereas GA-deactivated genes except GmGA2ox4 showed lower levels of expression. The transcript level of GmGA2ox4 encoding the only deactivation enzyme using C(20)-GAs as the substrates in soybean was dramatically enhanced in transgenic plants compared to that of wide type. Furthermore, the contents of endogenous bioactive GAs were significantly decreased in transgenic plants than those of wide type. The results suggested that AtDREB1A could cause dwarfism mediated by GA biosynthesis pathway in soybean.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of the gibberellin 2-oxidase gene from Torenia fournieri induces dwarf phenotypes in the liliaceous monocotyledon Tricyrtis sp.J Plant Physiol. 2013 Nov 1;170(16):1416-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 Jun 7. J Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23747060
-
dwarf and delayed-flowering 1, a novel Arabidopsis mutant deficient in gibberellin biosynthesis because of overexpression of a putative AP2 transcription factor.Plant J. 2004 Mar;37(5):720-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.2003.01998.x. Plant J. 2004. PMID: 14871311
-
Activation of gibberellin 2-oxidase 6 decreases active gibberellin levels and creates a dominant semi-dwarf phenotype in rice (Oryza sativa L.).J Genet Genomics. 2010 Jan;37(1):23-36. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(09)60022-9. J Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20171575
-
The DDF1 transcriptional activator upregulates expression of a gibberellin-deactivating gene, GA2ox7, under high-salinity stress in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2008 Nov;56(4):613-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03627.x. Epub 2008 Sep 19. Plant J. 2008. PMID: 18643985
-
The APETALA-2-like transcription factor OsAP2-39 controls key interactions between abscisic acid and gibberellin in rice.PLoS Genet. 2010 Sep 9;6(9):e1001098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001098. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20838584 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
DREB1A overexpression in transgenic chickpea alters key traits influencing plant water budget across water regimes.Plant Cell Rep. 2015 Feb;34(2):199-210. doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1699-z. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Plant Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25326370
-
Feedback transcription regulation between OsNAC3 and OsDREB1A promotes postgermination growth in rice.Sci Adv. 2025 Jun 27;11(26):eadw0421. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adw0421. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40577463 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter Implicated in Aluminum Tolerance in Wild Soybean (Glycine soja).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 9;22(24):13264. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413264. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948067 Free PMC article.
-
OsGA2ox5, a gibberellin metabolism enzyme, is involved in plant growth, the root gravity response and salt stress.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e87110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087110. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475234 Free PMC article.
-
AsHSP26.8a, a creeping bentgrass small heat shock protein integrates different signaling pathways to modulate plant abiotic stress response.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Apr 28;20(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02369-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32345221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fleet MC, Sun PT (2005) A DELLA cate balance: the role of gibberellins in plant morphogenesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8: 77–85. - PubMed
-
- Hedden P, Philips AL (2000) Gibberellin metabolism: New insights revealed by the genes. Trends Plant Sci 5: 523–530. - PubMed
-
- Han FM, Zhu B (2011) Evolutionary analysis of three gibberellin oxidase genes in rice,Arabidopsis and soybean. Gene 473: 43–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

