Comparison of optical and power Doppler ultrasound imaging for non-invasive evaluation of arsenic trioxide as a vascular disrupting agent in tumors
- PMID: 23029403
- PMCID: PMC3460997
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046106
Comparison of optical and power Doppler ultrasound imaging for non-invasive evaluation of arsenic trioxide as a vascular disrupting agent in tumors
Abstract
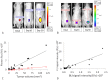
Small animal imaging provides diverse methods for evaluating tumor growth and acute response to therapy. This study compared the utility of non-invasive optical and ultrasound imaging to monitor growth of three diverse human tumor xenografts (brain U87-luc-mCherry, mammary MCF7-luc-mCherry, and prostate PC3-luc) growing in nude mice. Bioluminescence imaging (BLI), fluorescence imaging (FLI), and Power Doppler ultrasound (PD US) were then applied to examine acute vascular disruption following administration of arsenic trioxide (ATO).During initial tumor growth, strong correlations were found between manual caliper measured tumor volume and FLI intensity, BLI intensity following luciferin injection, and traditional B-mode US. Administration of ATO to established U87 tumors caused significant vascular shutdown within 2 hrs at all doses in the range 5 to 10 mg/kg in a dose dependant manner, as revealed by depressed bioluminescent light emission. At lower doses substantial recovery was seen within 4 hrs. At 8 mg/kg there was >85% reduction in tumor vascular perfusion, which remained depressed after 6 hrs, but showed some recovery after 24 hrs. Similar response was observed in MCF7 and PC3 tumors. Dynamic BLI and PD US each showed similar duration and percent reductions in tumor blood flow, but FLI showed no significant changes during the first 24 hrs.The results provide further evidence for comparable utility of optical and ultrasound imaging for monitoring tumor growth, More specifically, they confirm the utility of BLI and ultrasound imaging as facile assays of the vascular disruption in solid tumors based on ATO as a model agent.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Thorpe PE (2004) Vascular Targeting Agents as Cancer Therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res 10: 415–427. - PubMed
-
- Weis SM, Cheresh DA (2011) Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nature Med 17: 1359–1370. - PubMed
-
- Lew YS, Kolozsvary A, Brown SL, Kim JH (2002) Synergistic interaction with arsenic trioxide and fractionated radiation in locally advanced murine tumor. Cancer Res 62: 4202–4205. - PubMed
-
- Kim JH, Lew YS, Kolozsvary A, Ryu S, Brown SL (2003) Arsenic trioxide enhances radiation response of 9L glioma in the rat brain. Radiat Res 160: 662–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

