Fructose metabolism in humans - what isotopic tracer studies tell us
- PMID: 23031075
- PMCID: PMC3533803
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-89
Fructose metabolism in humans - what isotopic tracer studies tell us
Abstract
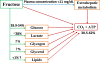
Fructose consumption and its implications on public health are currently under study. This work reviewed the metabolic fate of dietary fructose based on isotope tracer studies in humans. The mean oxidation rate of dietary fructose was 45.0% ± 10.7 (mean ± SD) in non-exercising subjects within 3-6 hours and 45.8% ± 7.3 in exercising subjects within 2-3 hours. When fructose was ingested together with glucose, the mean oxidation rate of the mixed sugars increased to 66.0% ± 8.2 in exercising subjects. The mean conversion rate from fructose to glucose was 41% ± 10.5 (mean ± SD) in 3-6 hours after ingestion. The conversion amount from fructose to glycogen remains to be further clarified. A small percentage of ingested fructose (<1%) appears to be directly converted to plasma TG. However, hyperlipidemic effects of larger amounts of fructose consumption are observed in studies using infused labeled acetate to quantify longer term de novo lipogenesis. While the mechanisms for the hyperlipidemic effect remain controversial, energy source shifting and lipid sparing may play a role in the effect, in addition to de novo lipogenesis. Finally, approximately a quarter of ingested fructose can be converted into lactate within a few of hours. The reviewed data provides a profile of how dietary fructose is utilized in humans.
Figures


References
-
- USDA-ERS. Food Availability: Spreadsheets-Added sugar and sweeteners. 2010. http://wwwersusdagov/Data/FoodConsumption/FoodAvailSpreadsheetshtm#sweets.
-
- Johnson RJ, Segal MS, Sautin Y, Nakagawa T, Feig DI, Kang DH, Gersch MS, Benner S, Sanchez-Lozada LG. Potential role of sugar (fructose) in the epidemic of hypertension, obesity and the metabolic syndrome, diabetes, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:899–906. - PubMed
-
- Bray GA, Nielsen SJ, Popkin BM. Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a role in the epidemic of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:537–543. - PubMed
-
- Teff KL, Elliott SS, Tschop M, Kieffer TJ, Rader D, Heiman M, Townsend RR, Keim NL, D'Alessio D, Havel PJ. Dietary fructose reduces circulating insulin and leptin, attenuates postprandial suppression of ghrelin, and increases triglycerides in women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2963–2972. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-031855. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Teff KL, Grudziak J, Townsend RR, Dunn TN, Grant RW, Adams SH, Keim NL, Cummings BP, Stanhope KL, Havel PJ. Endocrine and metabolic effects of consuming fructose- and glucose-sweetened beverages with meals in obese men and women: influence of insulin resistance on plasma triglyceride responses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1562–1569. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-2192. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

