A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 study of α4β2 agonist ABT-894 in adults with ADHD
- PMID: 23032073
- PMCID: PMC3547191
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2012.194
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 study of α4β2 agonist ABT-894 in adults with ADHD
Abstract
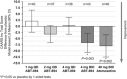
Dysregulation of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (NNR) system has been implicated in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and nicotinic agonists improve attention across preclinical species and humans. Hence, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study was designed to determine the safety and efficacy of a novel α4β2 NNR agonist (ABT-894 (3-(5,6-dichloro-pyridin-3-yl)-1(S),5 (S)-3,6-diazabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane)) in adults with ADHD. Participants (N=243) were randomized to one of four dose regimens of ABT-894 (1, 2, and 4 mg once daily (QD)) or 4 mg twice daily (BID) or the active comparator atomoxetine (40 mg BID) vs placebo for 28 days. Following a 2-week washout period, participants crossed over to the alternative treatment condition (active or placebo) for an additional 28 days. Primary efficacy was based on an investigator-rated Conners' Adult ADHD Rating Scale (CAARS:Inv) Total score at the end of each 4-week treatment period. Additional secondary outcome measures were assessed. A total of 238 patients were assessed for safety end points, 236 patients were included in the intent-to-treat data set, and 196 were included in the completers data set, which was the prespecified, primary data set for efficacy. Both the 4 mg BID ABT-894 and atomoxetine groups demonstrated significant improvement on the primary outcome compared with placebo. Several secondary outcome measures were also significantly improved with 4 mg BID ABT-894. Overall, ABT-894 was well tolerated at all dose levels. These results provide initial proof of concept for the use of α4β2 agonists in the treatment of adults with ADHD. Further investigation of ABT-894, including higher doses, is therefore warranted.
Figures



References
-
- Adler L, Dietrich A, Reimherr FW, Taylor LV, Sutton VK, Bakken R, et al. Safety and tolerability of once versus twice daily atomoxetine in adults with ADHD. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2006;18:107–113. - PubMed
-
- Adler L, Spencer T. The Adult ADHD Clinical Diagnostic Scale (ACDS) V 1.2. University School of Medicine: New York; 2004.
-
- Adler LA, Spencer T, McGough JJ, Jiang H, Muniz R. Long-term effectiveness and safety of dexmethylphenidate extended-release capsules in adult ADHD. J Atten Disord. 2009;12:449–459. - PubMed
-
- Apostol G, Abi-Saab W, Kratochvil CJ, Adler LA, Robieson WZ, Gault LM, et al. Efficacy and safety of the novel α4β2 neuronal nicotinic receptor partial agonist ABT-089 in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2012;219:715–725. - PubMed
-
- Barkley RA, Fischer M, Smallish L, Fletcher K. The persistence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder into young adulthood as a function of reporting source and definition of disorder. J Abnorm Psychol. 2002;111:279–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

