Combining fluorescent in situ hybridization data with ISS staging improves risk assessment in myeloma: an International Myeloma Working Group collaborative project
- PMID: 23032723
- PMCID: PMC3972006
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2012.282
Combining fluorescent in situ hybridization data with ISS staging improves risk assessment in myeloma: an International Myeloma Working Group collaborative project
Abstract
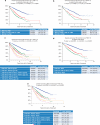
The combination of serum β2-microglobulin and albumin levels has been shown to be highly prognostic in myeloma as the International Staging System (ISS). The aim of this study was to assess the independent contributions of ISS stage and cytogenetic abnormalities in predicting outcomes. A retrospective analysis of international studies looking at both ISS and cytogenetic abnormalities was performed in order to assess the potential role of combining ISS stage and cytogenetics to predict survival. This international effort used the International Myeloma Working Group database of 12 137 patients treated worldwide for myeloma at diagnosis, of whom 2309 had cytogenetic studies and 5387 had analyses by fluorescent in situ hybridization (iFISH). Comprehensive analyses used 2642 patients with sufficient iFISH data available. Using the comprehensive iFISH data, combining both t(4;14) and deletion (17p), along with ISS stage, significantly improved the prognostic assessment in terms of progression-free survival and overall survival. The additional impact of patient age and use of high-dose therapy was also demonstrated. In conclusion, the combination of iFISH data with ISS staging significantly improves risk assessment in myeloma.
Figures


References
-
- Durie BG, Salmon SE, Moon TE. Pretreatment tumor mass, cell kinetics, and prognosis in multiple myeloma. Blood. 1980;55:364–372. - PubMed
-
- Bataille R, Durie BG, Grenier J, Sany J. Prognostic factors and staging in multiple myeloma: a reappraisal. J Clin Oncol. 1986;4:80–87. - PubMed
-
- Bataille R, Durie BG, Grenier J. Serum beta2 microglobulin and survival duration in multiple myeloma: a simple reliable marker for staging. Br J Haematol. 1983;55:439–447. - PubMed
-
- Bataille R, Boccadoro M, Klein B, Durie B, Pileri A. C-reactive protein and beta-2 microglobulin produce a simple and powerful myeloma staging system. Blood. 1992;80:733–737. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

