Quantum correlations with no causal order
- PMID: 23033068
- PMCID: PMC3493644
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2076
Quantum correlations with no causal order
Abstract
The idea that events obey a definite causal order is deeply rooted in our understanding of the world and at the basis of the very notion of time. But where does causal order come from, and is it a necessary property of nature? Here, we address these questions from the standpoint of quantum mechanics in a new framework for multipartite correlations that does not assume a pre-defined global causal structure but only the validity of quantum mechanics locally. All known situations that respect causal order, including space-like and time-like separated experiments, are captured by this framework in a unified way. Surprisingly, we find correlations that cannot be understood in terms of definite causal order. These correlations violate a 'causal inequality' that is satisfied by all space-like and time-like correlations. We further show that in a classical limit causal order always arises, which suggests that space-time may emerge from a more fundamental structure in a quantum-to-classical transition.
Figures
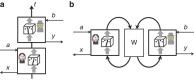
 (see text).
(see text).

 , where the set of matrices
, where the set of matrices  , with
, with  and
and  for
for  , provide a basis of
, provide a basis of  . We refer to terms of the form
. We refer to terms of the form  as of the type A1, terms of the form
as of the type A1, terms of the form  as of the type A1A2 and so on. In the Supplementary Information, we prove that a matrix satisfies condition (5) if it contains the terms listed in this table. Each of the terms can allow signalling in at most one direction and can be realized in a situation in which either Bob's actions are not in the causal past of Alice's
as of the type A1A2 and so on. In the Supplementary Information, we prove that a matrix satisfies condition (5) if it contains the terms listed in this table. Each of the terms can allow signalling in at most one direction and can be realized in a situation in which either Bob's actions are not in the causal past of Alice's  or vice versa
or vice versa  . The most general unidirectional process is a quantum channel with memory. Measurements of bipartite states that lead to non-signalling probabilities can be realized in both situations. The most general process matrix can contain terms from both rows and may not be decomposable into a mixture of quantum channels from Alice to Bob and from Bob to Alice.
. The most general unidirectional process is a quantum channel with memory. Measurements of bipartite states that lead to non-signalling probabilities can be realized in both situations. The most general process matrix can contain terms from both rows and may not be decomposable into a mixture of quantum channels from Alice to Bob and from Bob to Alice.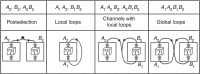
 , generated in our formalism by
, generated in our formalism by  . Notably, correlations of the type A1A2 have been exploited in models for describing CTCs. The pictures are only suggestive of the possible interpretations.
. Notably, correlations of the type A1A2 have been exploited in models for describing CTCs. The pictures are only suggestive of the possible interpretations.References
-
- Fivel D. I. How interference effects in mixtures determine the rules of quantum mechanics. Phys. Rev. A 50, 2108–2119 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Zeilinger A. A foundational principle for quantum mechanics. Found. Phys. 29, 631–643 (1999).
-
- Hardy L. Quantum Theory From Five Reasonable Axioms. Preprint at 〈arXiv:quant-ph/0101012〉 (2001).
-
- Clifton R., Bub J. & Halvorson H. Characterizing quantum theory in terms of information-theoretic constraints. Found. Phys. 33, 1561–1591 (2003).
-
- Goyal P., Knuth K. H. & Skilling J. Origin of complex quantum amplitudes and Feynman's rules. Phys. Rev. A 81, 022109 (2010).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

