Hypoxia/reoxygenation impairs memory formation via adenosine-dependent activation of caspase 1
- PMID: 23035103
- PMCID: PMC3476834
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0704-12.2012
Hypoxia/reoxygenation impairs memory formation via adenosine-dependent activation of caspase 1
Abstract
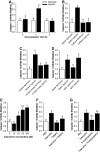
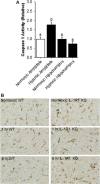
After hypoxia, a critical adverse outcome is the inability to create new memories. How anterograde amnesia develops or resolves remains elusive, but a link to brain-based IL-1 is suggested due to the vital role of IL-1 in both learning and brain injury. We examined memory formation in mice exposed to acute hypoxia. After reoxygenation, memory recall recovered faster than memory formation, impacting novel object recognition and cued fear conditioning but not spatially cued Y-maze performance. The ability of mice to form new memories after hypoxia/reoxygenation was accelerated in IL-1 receptor 1 knockout (IL-1R1 KO) mice, in mice receiving IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA), and in mice given the caspase 1 inhibitor Ac-YVAD-CMK. Mechanistically, hypoxia/reoxygenation more than doubled caspase 1 activity in the brain, which was localized to the amygdala compared to the hippocampus. This reoxygenation-dependent activation of caspase 1 was prevented by broad-spectrum adenosine receptor (AR) antagonism with caffeine and by targeted A1/A2A AR antagonism with 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine plus 3,7-dimethyl-1-propargylxanthine. Additionally, perfusion of adenosine activated caspase 1 in the brain, while caffeine blocked this action by adenosine. Finally, resolution of anterograde amnesia was improved by both caffeine and by targeted A1/A2A AR antagonism. These findings indicate that amygdala-based anterograde amnesia after hypoxia/reoxygenation is sustained by IL-1β generated through adenosine-dependent activation of caspase 1 after reoxygenation.
Figures




References
-
- Avivi A, Brodsky L, Nevo E, Band MR. Differential expression profiling of the blind subterranean mole rat Spalax ehrenbergi superspecies: bioprospecting for hypoxia tolerance. Physiol Genomics. 2006;27:54–64. - PubMed
-
- Bauernfeind FG, Horvath G, Stutz A, Alnemri ES, MacDonald K, Speert D, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Monks BG, Fitzgerald KA, Hornung V, Latz E. Cutting edge: NF-kappaB activating pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J Immunol. 2009;183:787–791. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beatty WW, Salmon DP, Bernstein N, Martone M, Lyon L, Butters N. Procedural learning in a patient with amnesia due to hypoxia. Brain Cogn. 1987;6:386–402. - PubMed
-
- Berggren D, Gustafson Y, Eriksson B, Bucht G, Hansson LI, Reiz S, Winblad B. Postoperative confusion after anesthesia in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures. Anesth Analg. 1987;66:497–504. - PubMed
-
- Bickler PE, Hansen BM. Causes of calcium accumulation in rat cortical brain slices during hypoxia and ischemia: role of ion channels and membrane damage. Brain Res. 1994;665:269–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
