EndoPredict improves the prognostic classification derived from common clinical guidelines in ER-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer
- PMID: 23035151
- PMCID: PMC3574544
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mds334
EndoPredict improves the prognostic classification derived from common clinical guidelines in ER-positive, HER2-negative early breast cancer
Abstract
Background: In early estrogen receptor (ER)-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer, the decision to administer chemotherapy is largely based on prognostic criteria. The combined molecular/clinical EndoPredict test (EPclin) has been validated to accurately assess prognosis in this population. In this study, the clinical relevance of EPclin in relation to well-established clinical guidelines is assessed.
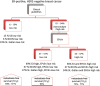
Patients and methods: We assigned risk groups to 1702 ER-positive/HER2-negative postmenopausal women from two large phase III trials treated only with endocrine therapy. Prognosis was assigned according to National Comprehensive Cancer Center Network-, German S3-, St Gallen guidelines and the EPclin. Prognostic groups were compared using the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis.
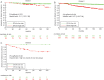
Results: After 10 years, absolute risk reductions (ARR) between the high- and low-risk groups ranged from 6.9% to 11.2% if assigned according to guidelines. It was at 18.7% for EPclin. EPclin reassigned 58%-61% of women classified as high-/intermediate-risk (according to clinical guidelines) to low risk. Women reclassified to low risk showed a 5% rate of distant metastasis at 10 years.
Conclusion: The EPclin score is able to predict favorable prognosis in a majority of patients that clinical guidelines would assign to intermediate or high risk. EPclin may reduce the indications for chemotherapy in ER-positive postmenopausal women with a limited number of clinical risk factors.
Figures



References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365:1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, et al. Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1784–1792. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Jeong JH, Bryant J, et al. Treatment of lymph-node-negative, oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer: long-term findings from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project randomised clinical trials. Lancet. 2004;364:858–868. - PubMed
-
- Carlson RW, Brown E, Burstein HJ, et al. NCCN task force report: adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2006;4(Suppl 1):S1–S26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

