Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a cause for rare but fatal outcome in tuberculosis
- PMID: 23035171
- PMCID: PMC4544015
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-006982
Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a cause for rare but fatal outcome in tuberculosis
Abstract
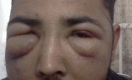
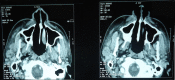
Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), also called haemophagocytic syndrome (HPS) is characterised by a dysregulated activation and proliferation of macrophages, leading to uncontrolled phagocytosis of platelets, erythrocytes, lymphocytes and their haematopoietic precursors throughout the reticuloendothelial system. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-associated HPS is a rare and underdiagnosed association. We report a 34-year-old male patient diagnosed with tubercular pleural effusion responding poorly to antitubercular treatment. Patient later developed generalised lymphadenopathy, pancytopaenia and liver dysfunction and was eventually diagnosed as HLH. Despite being treated as per HLH protocol 2004 he could not be saved.
Figures


References
-
- Brastianos PK, Swanson JW, Tobenson M, et al. Tuberculosis-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis 2006;447–54. - PubMed
-
- Henter JI, Elinder G, Söder O, et al. Incidence in Sweden and clinical features of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Acta Paediatr Scand 1991;80:428–35. - PubMed
-
- Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, et al. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2007;48:124–31. - PubMed
-
- Chan JK, Ng CS, Law Ck, et al. Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome: a study of seven fatal cases. Pathology 1987;19:43–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
