Identification of Streptococcus intermedius central nervous system infection by use of PCR and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- PMID: 23035188
- PMCID: PMC3502992
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01296-12
Identification of Streptococcus intermedius central nervous system infection by use of PCR and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
Abstract
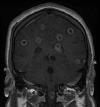
We describe the utility of PCR and electrospray ionization with mass spectrometry (PCR/ESI-MS) of culture-negative cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in order to identify Gram-positive cocci noted on a Gram stain of CSF from a previously healthy 26-year-old man with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and multiple brain abscesses. CSF samples were obtained 2 weeks apart, first by lumbar puncture and 2 weeks later from an external ventricular drain that was inserted into the right ventricle. Both CSF cultures were negative. A Gram stain of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid was notable for many Gram-positive cocci (GPC), but cultures of BAL fluid and subcarinal lymph node biopsy tissue were negative. PCR/ESI-MS detected Streptococcus intermedius, a common cause of brain abscesses, in both CSF samples as well as in the fixed tissue from the biopsy. This unique case confirms S. intermedius pulmonary infection as the source of metastatic CNS infection and reveals the potential of PCR/ESI-MS to detect a streptococcal pathogen not captured by conventional cultures.
Figures
References
-
- Carpenter J, Stapleton S, Holliman R. 2007. Retrospective analysis of 49 cases of brain abscess and review of the literature. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 26:1–11 - PubMed
-
- Chun CH, Johnson JD, Hofstetter M, Raff MJ. 1986. Brain abscess. A study of 45 consecutive cases. Medicine 65:415–431 - PubMed
-
- Reference deleted.
-
- Hofstadler SA, Sampath R, Blyn LB, Eshoo MW, Hall TA. 2005. TIGER: the universal biosensor. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 242:23–41
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous