The Thai Phase III HIV Type 1 Vaccine trial (RV144) regimen induces antibodies that target conserved regions within the V2 loop of gp120
- PMID: 23035746
- PMCID: PMC3484815
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2012.0103
The Thai Phase III HIV Type 1 Vaccine trial (RV144) regimen induces antibodies that target conserved regions within the V2 loop of gp120
Abstract
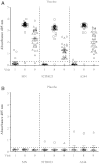
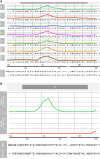
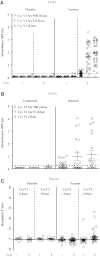
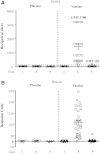
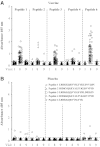
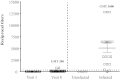
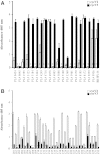
The Thai Phase III clinical trial (RV144) showed modest efficacy in preventing HIV-1 acquisition. Plasma collected from HIV-1-uninfected trial participants completing all injections with ALVAC-HIV (vCP1521) prime and AIDSVAX B/E boost were tested for antibody responses against HIV-1 gp120 envelope (Env). Peptide microarray analysis from six HIV-1 subtypes and group M consensus showed that vaccination induced antibody responses to the second variable (V2) loop of gp120 of multiple subtypes. We further evaluated V2 responses by ELISA and surface plasmon resonance using cyclic (Cyc) and linear V2 loop peptides. Thirty-one of 32 vaccine recipients tested (97%) had antibody responses against Cyc V2 at 2 weeks postimmunization with a reciprocal geometric mean titer (GMT) of 1100 (range: 200-3200). The frequency of detecting plasma V2 antibodies declined to 19% at 28 weeks post-last injection (GMT: 110, range: 100-200). Antibody responses targeted the mid-region of the V2 loop that contains conserved epitopes and has the amino acid sequence KQKVHALFYKLDIVPI (HXB2 Numbering sequence 169-184). Valine at position 172 was critical for antibody binding. The frequency of V3 responses at 2 weeks postimmunization was modest (18/32, 56%) with a GMT of 185 (range: 100-800). In contrast, naturally infected HIV-1 individuals had a lower frequency of antibody responses to V2 (10/20, 50%; p=0.003) and a higher frequency of responses to V3 (19/20, 95%), with GMTs of 400 (range: 100-3200) and 3570 (range: 200-12,800), respectively. RV144 vaccination induced antibodies that targeted a region of the V2 loop that contains conserved epitopes. Early HIV-1 transmission events involve V2 loop interactions, raising the possibility that anti-V2 antibodies in RV144 may have contributed to viral inhibition.
Figures

References
-
- Rerks-Ngarm S. Pitisuttithum P. Nitayaphan S, et al. Vaccination with ALVAC and AIDSVAX to prevent HIV-1 infection in Thailand. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(23):2209–2220. - PubMed
-
- Nitayaphan S. Pitisuttithum P. Karnasuta C, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an HIV subtype B and E prime-boost vaccine combination in HIV-negative Thai adults. J Infect Dis. 2004;190(4):702–706. - PubMed
-
- Karnasuta C. Paris RM. Cox JH, et al. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic responses in participants enrolled in a phase I/II ALVAC-HIV/AIDSVAX B/E prime-boost HIV-1 vaccine trial in Thailand. Vaccine. 2005;23(19):2522–2529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

