Gadolinium MRI contrast agents based on triazine dendrimers: relaxivity and in vivo pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 23035964
- PMCID: PMC3586605
- DOI: 10.1021/bc300461r
Gadolinium MRI contrast agents based on triazine dendrimers: relaxivity and in vivo pharmacokinetics
Abstract
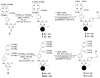
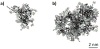
Four gadolinium (Gd)-based macromolecular contrast agents, G3-(Gd-DOTA)(24), G5-(Gd-DOTA)(96), G3-(Gd-DTPA)(24), and G5-(Gd-DTPA)(96), were prepared that varied in the size of dendrimer (generation three and five), the type of chelate group (DTPA or DOTA), and the theoretical number of metalated chelates (24 and 96). Synthesis relied on a dichlorotriazine derivatized with a DOTA or DTPA ligand that was incorporated into the dendrimer and ultimately metalated with Gd ions. Paramagnetic characteristics and in vivo pharmacokinetics of all four contrast agents were investigated. The DOTA-containing agents, G3-(Gd-DOTA)(24) and G5-(Gd-DOTA)(96), demonstrated exceptionally high r1 relaxivity values at off-peak magnetic fields. Additionally, G5-(Gd-DOTA)(96) showed increased r1 relaxivity in serum compared to that in PBS, which was consistent with in vivo images. While G3-(Gd-DOTA)(24) and G3-(Gd-DTPA)(24) were rapidly excreted into the urine, G5-(Gd-DOTA)(96) and G5-(Gd-DTPA)(96) did not clear as quickly through the kidneys. Molecular simulation of the DOTA-containing dendrimers suggests that a majority of the metalated ligands are accessible to water. These triazine dendrimer-based MRI contrast agents exhibit several promising features such as high in vivo r1 relaxivity, desirable pharmacokinetics, and well-defined structure.
Figures

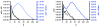




References
-
- Menjoge AR, Kannan RM, Tomalia DA. Dendrimer-based drug and imaging conjugates: design considerations for nanomedical applications. Drug Discov Today. 2010;15:171–185. - PubMed
-
- Bryant LH, Jr, Brechbiel MW, Wu C, Bulte JW, Herynek V, Frank JA. Synthesis and relaxometry of high-generation (G = 5, 7, 9, and 10) PAMAM dendrimer-DOTA-gadolinium chelates. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1999;9:348–352. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi H, Sato N, Hiraga A, Saga T, Nakamoto Y, Ueda H, Konishi J, Togashi K, Brechbiel MW. 3D-micro-MR angiography of mice using macromolecular MR contrast agents with polyamidoamine dendrimer core with references to their pharmacokinetic properties. Magn Reson Med. 2001;45:454–460. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi H, Sato N, Kawamoto S, Saga T, Hiraga A, Ishimori T, Konishi J, Togashi K, Brechbiel MW. 3D MR angiography of intratumoral vasculature using a novel macromolecular MR contrast agent. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46:579–585. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

