The inflammatory response in sepsis
- PMID: 23036432
- PMCID: PMC3543471
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2012.09.004
The inflammatory response in sepsis
Abstract
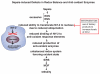
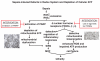
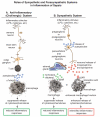
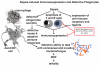
The pathophysiology of sepsis and its accompanying systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and the events that lead to multiorgan failure and death are poorly understood. It is known that, in septic humans and rodents, the development of SIRS is associated with a loss of the redox balance, but SIRS can also develop in noninfectious states. In addition, a hyperinflammatory state develops, together with impaired innate immune functions of phagocytes, immunosuppression, and complement activation, collectively leading to septic shock and lethality. Here, we discuss recent insights into the signaling pathways in immune and phagocytic cells that underlie sepsis and SIRS and consider how these might be targeted for therapeutic interventions to reverse or attenuate pathways that lead to lethality during sepsis.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Martin GS, et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Coopersmith CM, et al. A comparison of critical care research funding and the financial burden of critical illness in the United States*. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:1072–1079. - PubMed
-
- [Accessed November 18, 2011];Xigris [drotegogin alfa (activated)]: market withdrawal-failure survival benefit. 2011 www.fda.gov/Safety/Medwatch/Safety/Information/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedic.... Posted October 25, 2011.
-
- Angus DC. The search for effective therapy for sepsis: back to the drawing board? JAMA. 2011;306:2614–2615. - PubMed
-
- Erridge C. Endogenous ligands of TLR2 and TLR4: agonists or assistants? J Leukoc Biol. 2010;87:989–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

