[Clinical practice guideline on the management of patients with dyspepsia. Update 2012]
- PMID: 23036729
- PMCID: PMC7025630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aprim.2012.05.003
[Clinical practice guideline on the management of patients with dyspepsia. Update 2012]
Abstract
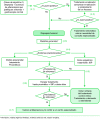
The aim of the Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) on the Management of Patients with Dyspepsia is to generate recommendations on the optimal approach to dyspepsia in the primary care and specialized outpatient setting. The main objective of this CPG is to help to optimize the diagnostic process, identifying patients with a low risk of a serious organic disease (mainly tumoral), who could be safely managed without the need for invasive diagnostic tests and/or referral to a specialist. The importance of this aim lies in the need to accurately diagnose patients with esophagogastric cancer and correctly treat peptic ulcer while, at the same time, reduce negative endoscopies in order to appropriately use the available healthcare resources. This CPG reviews the initial strategies that can be used in patients with uninvestigated dyspepsia and evaluates the possible decision to begin empirical therapy or to investigate the existence of a lesion that could explain the symptoms. This CPG also discusses functional dyspepsia, which encompasses all patients with dyspepsia with no demonstrable cause on endoscopy. Recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of peptic ulcer and Helicobacter pylori infection are also made. To classify the scientific evidence and strengthen the recommendations, the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation Working Group) system has been used (http://www.gradeworkinggroup.org/).
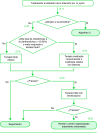
La finalidad de la Guía de Práctica Clínica (GPC) sobre el Manejo del Paciente con Dispepsia es generar unas recomendaciones acerca del manejo óptimo de la dispepsia en el ámbito de la atención primaria y especializada ambulatoria. Su objetivo principal es ayudar a optimizar el proceso diagnóstico, identificando a los pacientes con bajo riesgo de tener una patología orgánica grave (fundamentalmente tumoral), los cuales podrían ser manejados de forma segura sin necesidad de realizar pruebas diagnósticas invasivas y/o derivaciones al especialista. La importancia de este objetivo radica en la necesidad de no dejar de diagnosticar a los pacientes con un cáncer esófago-gástrico, tratar correctamente la úlcera péptica y, a la vez, reducir las endoscopias negativas para, en definitiva, utilizar de manera adecuada los recursos sanitarios disponibles.
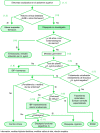
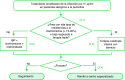
En esta GPC se revisan las posibles estrategias iniciales en el paciente con dispepsia no investigada, valorando la posible decisión de iniciar o no un tratamiento empírico o de investigar la existencia de una lesión que justifique los síntomas. Asimismo, en esta GPC se aborda la dispepsia funcional, la cual engloba a todos los pacientes con dispepsia sin una causa orgánica objetivable a través de la endoscopia. En esta GPC también se presentan las recomendaciones para el diagnóstico y tratamiento de la úlcera péptica y de la infección por Helicobacter pylori.
Para clasificar la evidencia científica y la fuerza de las recomendaciones se ha utilizado el sistema GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation Working Group) (
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier España, S.L. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Grupo de trabajo sobre GPC . Plan Nacional para el SNS del MSC. Instituto Aragonés de Ciencias de la Salud-I + CS; Madrid: 2007. Elaboración de Guías de Práctica Clínica en el Sistema Nacional de Salud. Manual Metodológico. Guías de Práctica Clínica en el SNS: I+CS No 2006/0I.
-
- Gisbert J.P., Alonso-Coello P., Piqué J.M. [How can we find, design, evaluate and use clinical practice guidelines?.] Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;31:239–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical