Warts and all: human papillomavirus in primary immunodeficiencies
- PMID: 23036745
- PMCID: PMC3517887
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.049
Warts and all: human papillomavirus in primary immunodeficiencies
Abstract
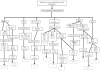
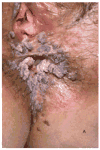
Infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) is almost universal and eventually asymptomatic, but pathologic infection with HPV is severe, recurrent, and recalcitrant to therapy. It is also an underappreciated manifestation of primary immunodeficiency. Mutations in EVER1, EVER2, GATA2, CXCR4, and dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) are typically associated with extensive HPV infections, whereas several other primary immune defects result in severe HPV much less frequently. We review immunodeficiencies with severe HPV infections and the mechanisms underlying them.
Published by Mosby, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Sterling JC, Handfield-Jones S, Hudson PM. Guidelines for the management of cutaneous warts. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:4–11. - PubMed
-
- van Haalen FM, Bruggink SC, Gussekloo J, Assendelft WJ, Eekhof JA. Warts in primary schoolchildren: prevalence and relation with environmental factors. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161:148–52. - PubMed
-
- Williams HC, Pottier A, Strachan D. The descriptive epidemiology of warts in British schoolchildren. Br J Dermatol. 1993;128:504–11. - PubMed
-
- Kainz JT, Kozel G, Haidvogl M, Smolle J. Homoeopathic versus placebo therapy of children with warts on the hands: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Dermatology. 1996;193:318–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

