Impaired myogenesis in estrogen-related receptor γ (ERRγ)-deficient skeletal myocytes due to oxidative stress
- PMID: 23038752
- PMCID: PMC3528312
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.12-212290
Impaired myogenesis in estrogen-related receptor γ (ERRγ)-deficient skeletal myocytes due to oxidative stress
Abstract
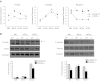
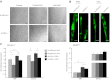
Specialized contractile function and increased mitochondrial number and oxidative capacity are hallmark features of myocyte differentiation. The estrogen-related receptors (ERRs) can regulate mitochondrial biogenesis or mitochondrial enzyme expression in skeletal muscle, suggesting that ERRs may have a role in promoting myogenesis. Therefore, we characterized myogenic programs in primary myocytes isolated from wild-type (M-ERRγWT) and muscle-specific ERRγ(-/-) (M-ERRγ(-/-)) mice. Myotube maturation and number were decreased throughout differentiation in M-ERRγ(-/-) primary myocytes, resulting in myotubes with reduced mitochondrial content and sarcomere assembly. Compared with M-ERRγWT myocytes at the same differentiation stage, the glucose oxidation rate was reduced by 30% in M-ERRγ(-/-) myotubes, while medium-chain fatty acid oxidation was increased by 34% in M-ERRγ(-/-) myoblasts and 36% in M-ERRγ(-/-) myotubes. Concomitant with increased reliance on mitochondrial β-oxidation, H(2)O(2) production was significantly increased by 40% in M-ERRγ(-/-) myoblasts and 70% in M-ERRγ(-/-) myotubes compared to M-ERRγWT myocytes. ROS activation of FoxO and NF-κB and their downstream targets, atrogin-1 and MuRF1, was observed in M-ERRγ(-/-) myocytes. The antioxidant N-acetyl cysteine rescued myotube formation and atrophy gene induction in M-ERRγ(-/-) myocytes. These results suggest that loss of ERRγ causes metabolic defects and oxidative stress that impair myotube formation through activation of skeletal muscle atrophy pathways.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Estrogen-related receptor α regulates skeletal myocyte differentiation via modulation of the ERK MAP kinase pathway.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):C630-45. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00033.2011. Epub 2011 May 11. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21562305 Free PMC article.
-
O-GlcNAcase deficiency suppresses skeletal myogenesis and insulin sensitivity in mice through the modulation of mitochondrial homeostasis.Diabetologia. 2016 Jun;59(6):1287-96. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3919-2. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 26993634
-
Estrogen-related receptor-α (ERRα) deficiency in skeletal muscle impairs regeneration in response to injury.FASEB J. 2014 Mar;28(3):1082-97. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-229211. Epub 2013 Nov 25. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24277576 Free PMC article.
-
Looking beyond PGC-1α: emerging regulators of exercise-induced skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and their activation by dietary compounds.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020 Jan;45(1):11-23. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2019-0069. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020. PMID: 31158323 Review.
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress in Skeletal Muscle Myogenesis and Muscle Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 11;11(4):755. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040755. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453440 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Muscle-specific ERRγ activation mitigates muscle atrophy after ACL injury.FASEB J. 2025 Feb 28;39(4):e70409. doi: 10.1096/fj.202402021R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 39964243 Free PMC article.
-
ERRγ is downregulated in injured motor neuron subpopulations following brachial plexus root avulsion.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jan;19(1):205-213. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8209. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 31853291 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Estrogen Signaling in the Radiation-induced Neurodegeneration: A Possible Role of Phytoestrogens.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(2):353-379. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220310115004. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 35272592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of stably expandable induced myogenic stem cells by four transcription factors.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 25;9(11):1092. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1114-8. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30361642 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of In Ovo Supplementation with Nanonutrition (L-Arginine Conjugated with Ag NPs) on Muscle Growth, Immune Response and Heat Shock Proteins at Different Chicken Embryonic Development Stages.Animals (Basel). 2020 Mar 27;10(4):564. doi: 10.3390/ani10040564. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32230934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huss J. M., Kopp R. P., Kelly D. P. (2002) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) coactivates the cardiac-enriched nuclear receptors estrogen-related receptor-alpha and -gamma. Identification of novel leucine-rich interaction motif within PGC-1alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 40265–40274 - PubMed
-
- Kamei Y., Ohizumi H., Fujitani Y., Nemoto T., Tanaka T., Takahashi N., Kawada T., Miyoshi M., Ezaki O., Kakizuka A. (2003) PPARgamma coactivator 1β/ERR ligand 1 is an ERR protein ligand, whose expression induces a high-energy expenditure and antagonizes obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 12378–12383 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Laganiere J., Tremblay G. B., Dufour C. R., Giroux S., Rousseau F., Giguere V. (2004) A polymorphic autoregulatory hormone response element in the human estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα) promoter dictates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha control of ERRalpha expression. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 18504–18510 - PubMed
-
- Schreiber S. N., Emter R., Hock M. B., Knutti D., Cardenas J., Podvinec M., Oakeley E. J., Kralli A. (2004) The estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha) functions in PPARgamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1α)-induced mitochondrial biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 6472–6477 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dufour C. R., Wilson B. J., Huss J. M., Kelly D. P., Alaynick W. A., Downes M., Evans R. M., Blanchette M., Giguere V. (2007) Genome-wide orchestration of cardiac functions by the orphan nuclear receptors ERRalpha and gamma. Cell Metab. 5, 345–356 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

