Neuromodulation of neuronal circuits: back to the future
- PMID: 23040802
- PMCID: PMC3482119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.010
Neuromodulation of neuronal circuits: back to the future
Abstract
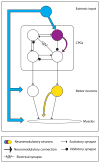
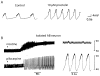
All nervous systems are subject to neuromodulation. Neuromodulators can be delivered as local hormones, as cotransmitters in projection neurons, and through the general circulation. Because neuromodulators can transform the intrinsic firing properties of circuit neurons and alter effective synaptic strength, neuromodulatory substances reconfigure neuronal circuits, often massively altering their output. Thus, the anatomical connectome provides a minimal structure and the neuromodulatory environment constructs and specifies the functional circuits that give rise to behavior.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Adams ME, O’Shea M. Peptide cotransmitter at a neuromuscular junction. Science. 1983;221:286–288. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann CI. Beyond the connectome: how neuromodulators shape neural circuits. Bioessays. 2012;34:458–465. - PubMed
-
- Barker DL, Molinoff PB, Kravitz EA. Octopamine in the lobster nervous system. Nature New Biol. 1972;236:61–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

