Dopaminergic modulation of synaptic transmission in cortex and striatum
- PMID: 23040805
- PMCID: PMC4386589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.023
Dopaminergic modulation of synaptic transmission in cortex and striatum
Abstract
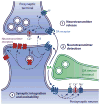
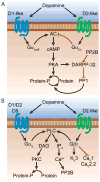
Among the many neuromodulators used by the mammalian brain to regulate circuit function and plasticity, dopamine (DA) stands out as one of the most behaviorally powerful. Perturbations of DA signaling are implicated in the pathogenesis or exploited in the treatment of many neuropsychiatric diseases, including Parkinson's disease (PD), addiction, schizophrenia, obsessive compulsive disorder, and Tourette's syndrome. Although the precise mechanisms employed by DA to exert its control over behavior are not fully understood, DA is known to regulate many electrical and biochemical aspects of neuronal function including excitability, synaptic transmission, integration and plasticity, protein trafficking, and gene transcription. In this Review, we discuss the actions of DA on ionic and synaptic signaling in neurons of the prefrontal cortex and striatum, brain areas in which dopaminergic dysfunction is thought to be central to disease.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Dopamine neurons are multi-neurotransmitter neurons.Mov Disord. 2013 Aug;28(9):1211. doi: 10.1002/mds.25531. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Mov Disord. 2013. PMID: 23925922 No abstract available.
References
-
- Andre VM, Cepeda C, Cummings DM, Jocoy EL, Fisher YE, William Yang X, Levine MS. Dopamine modulation of excitatory currents in the striatum is dictated by the expression of D1 or D2 receptors and modified by endocannabinoids. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;31:14–28. - PubMed
-
- Aosaki T, Graybiel AM, Kimura M. Effect of the nigrostriatal dopamine system on acquired neural responses in the striatum of behaving monkeys. Science. 1994;265:412–415. - PubMed
-
- Bamford NS, Zhang H, Schmitz Y, Wu NP, Cepeda C, Levine MS, Schmauss C, Zakharenko SS, Zablow L, Sulzer D. Heterosynaptic dopamine neurotransmission selects sets of corticostriatal terminals. Neuron. 2004;42:653–663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

