Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function
- PMID: 23040807
- PMCID: PMC3517813
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.020
Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function
Abstract
Endocannabinoids are key modulators of synaptic function. By activating cannabinoid receptors expressed in the central nervous system, these lipid messengers can regulate several neural functions and behaviors. As experimental tools advance, the repertoire of known endocannabinoid-mediated effects at the synapse, and their underlying mechanism, continues to expand. Retrograde signaling is the principal mode by which endocannabinoids mediate short- and long-term forms of plasticity at both excitatory and inhibitory synapses. However, growing evidence suggests that endocannabinoids can also signal in a nonretrograde manner. In addition to mediating synaptic plasticity, the endocannabinoid system is itself subject to plastic changes. Multiple points of interaction with other neuromodulatory and signaling systems have now been identified. In this Review, we focus on new advances in synaptic endocannabinoid signaling in the mammalian brain. The emerging picture not only reinforces endocannabinoids as potent regulators of synaptic function but also reveals that endocannabinoid signaling is mechanistically more complex and diverse than originally thought.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
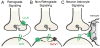
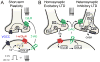
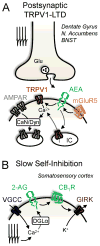

References
-
- Alger BE. Retrograde signaling in the regulation of synaptic transmission: focus on endocannabinoids. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;68:247–286. - PubMed
-
- Auclair N, Otani S, Soubrie P, Crepel F. Cannabinoids modulate synaptic strength and plasticity at glutamatergic synapses of rat prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2000;83:3287–3293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

