Effects of ezetimibe added to statin therapy on markers of cholesterol absorption and synthesis and LDL-C lowering in hyperlipidemic patients
- PMID: 23040830
- PMCID: PMC3749834
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.09.001
Effects of ezetimibe added to statin therapy on markers of cholesterol absorption and synthesis and LDL-C lowering in hyperlipidemic patients
Abstract
Objective: Statins inhibit cholesterol synthesis but can upregulate cholesterol absorption, with higher doses producing larger effects. Ezetimibe inhibits cholesterol absorption but also upregulates synthesis. We tested whether ezetimibe added to on-going statin therapy would be most effective in lowering LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) in subjects on high-potency statins and whether these effects would be related to alterations in cholesterol absorption (β-sitosterol) and synthesis (lathosterol) markers.
Methods: Hypercholesterolemic subjects (n = 874) on statins received ezetimibe 10 mg/day. Plasma lipids, lathosterol, and β-sitosterol were measured at baseline and on treatment. Subjects were divided into low- (n = 133), medium- (n = 582), and high- (n = 159) statin potency groups defined by predicted LDL-C-lowering effects of each ongoing statin type and dose (reductions of ~20-30%, ~31-45%, or ~46-55%, respectively).
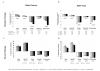
Results: The high-potency group had significantly lower baseline lathosterol (1.93 vs. 2.58 vs. 3.17 μmol/l; p < 0.001) and higher baseline β-sitosterol values (6.21 vs. 4.58 vs. 4.51 μmol/l, p < 0.001) than medium-/low-potency groups. Ezetimibe treatment in the high-potency group produced significantly greater reductions from baseline in LDL-C than medium-/low-potency groups (-29.1% vs. -25.0% vs. -22.7%; p < 0.001) when evaluating unadjusted data. These effects and group differences were significantly (p < 0.05) related to greater β-sitosterol reductions and smaller lathosterol increases. However, LDL-C reduction differences between groups were no longer significant after controlling for placebo effects, due mainly to modest LDL-C lowering by placebo in the high-potency group.
Conclusion: Patients on high-potency statins have the lowest levels of cholesterol synthesis markers and the highest levels of cholesterol absorption markers at baseline, and the greatest reduction in absorption markers and the smallest increases in synthesis markers with ezetimibe addition. Therefore, such patients may be good candidates for ezetimibe therapy if additional LDL-C lowering is needed.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00092586.
Copyright © 2012 Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

baseline lathosterol/cholesterol
baseline β-sitosterol/cholesterol
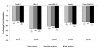
References
-
- Jones PH, Davidson MH, Stein EA, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin, simvastatin, and pravastatin across doses (STELLAR Trial) Am J Cardiol. 2003;92:152–160. - PubMed
-
- Weng TC, Yang YH, Lin SJ, Tai SH. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the therapeutic equivalence of statins. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2010;35:139–151. - PubMed
-
- Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002;106:3143–3421. - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, et al. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Circulation. 2004;110:227–239. - PubMed
-
- Catapano AL, Reiner Z, De Backer G, et al. ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) Atherosclerosis. 2011;217:3–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

