Ephrin-B2 reverse signaling is required for topography but not pattern formation of lateral superior olivary inputs to the inferior colliculus
- PMID: 23042409
- PMCID: PMC4019236
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.23243
Ephrin-B2 reverse signaling is required for topography but not pattern formation of lateral superior olivary inputs to the inferior colliculus
Abstract
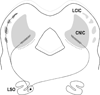
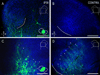
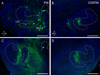
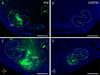
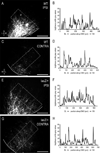
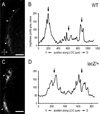
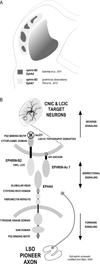
Graded and modular expressions of Eph-ephrins are known to provide positional information for the formation of topographic maps and patterning in the developing nervous system. Previously we have shown that ephrin-B2 is expressed in a continuous gradient across the tonotopic axis of the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus (CNIC), whereas patterns are discontinuous and modular in the lateral cortex of the IC (LCIC). The present study explores the involvement of ephrin-B2 signaling in the development of projections to the CNIC and LCIC arising from the lateral superior olivary nuclei (LSO) prior to hearing onset. Anterograde and retrograde fluorescent tracing methods in neonatal fixed tissue preparations were used to compare topographic mapping and the establishment of LSO layers/modules in wild-type and ephrin-B2(lacZ/+) mice (severely compromised reverse signaling). At birth, pioneer LSO axons occupy the ipsilateral IC in both groups but are delayed contralaterally in ephrin-B2(lacZ/+) mutants. By the onset of hearing, both wild-type and mutant projections form discernible layers bilaterally in the CNIC and modular arrangements within the ipsilateral LCIC. In contrast, ephrin-B2(lacZ/+) mice lack a reliable topography in LSO-IC projections, suggesting that fully functional ephrin-B2 reverse signaling is required for normal projection mapping. Taken together, these ephrin-B2 findings paired with known coexpression of EphA4 suggest the importance of these signaling proteins in establishing functional auditory circuits prior to experience.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chernock ML, Larue DT, Winer JA. A periodic network of neurochemical modules in the inferior colliculus. Hear Res. 2004;188:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Coleman JR, Clerici WJ. Sources of projections to subdivisions of the inferior colliculus in rat. J Comp Neurol. 1987;262:215–226. - PubMed
-
- Cowan CA, Henkemeyer M. Ephrins in reverse, park and drive. Trends Cell Biol. 2002;12:339–346. - PubMed
-
- Cramer KS. Eph proteins and the assembly of auditory circuits. Hear Res. 2005;206:42–51. - PubMed
-
- Cutforth T, Moring L, Mendelsohn M, Nemes A, Shah NM, Kim MM, Frisén J, Axel R. Axonal ephrin-As and odorant receptors: coordinate determination of the olfactory sensory map. Cell. 2003;114:311–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

