Lipid peroxidation triggers neurodegeneration: a redox proteomics view into the Alzheimer disease brain
- PMID: 23044265
- PMCID: PMC3573239
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.09.027
Lipid peroxidation triggers neurodegeneration: a redox proteomics view into the Alzheimer disease brain
Abstract
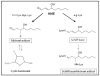
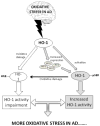
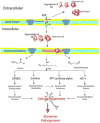
Lipid peroxidation involves a cascade of reactions in which production of free radicals occurs selectively in the lipid components of cellular membranes. Polyunsaturated fatty acids easily undergo lipid peroxidation chain reactions, which, in turn, lead to the formation of highly reactive electrophilic aldehydes. Among these, the most abundant aldehydes are 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) and malondialdehyde, while acrolein is the most reactive. Proteins are susceptible to posttranslational modifications caused by aldehydes binding covalently to specific amino acid residues, in a process called Michael adduction, and these types of protein adducts, if not efficiently removed, may be, and generally are, dangerous for cellular homeostasis. In the present review, we focused the discussion on the selective proteins that are identified, by redox proteomics, as selective targets of HNE modification during the progression and pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease (AD). By comparing results obtained at different stages of the AD, it may be possible to identify key biochemical pathways involved and ideally identify therapeutic targets to prevent, delay, or treat AD.
Keywords: 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal; ATP synthase; Collapsin regulatory protein 2; Enolase; Lipid peroxidation; Oxidative stress; Proteomics.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Esterbauer H, Schaur RJ, Zollner H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;11:81–128. - PubMed
-
- Pryor WA, Porter NA. Suggested mechanisms for the production of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal from the autoxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;8:541–3. - PubMed
-
- Loidl-Stahlhofen A, Hannemann K, Spiteller G. Generation of alpha-hydroxyaldehydic compounds in the course of lipid peroxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1213:140–8. - PubMed
-
- Musiek ES, Yin H, Milne GL, Morrow JD. Recent advances in the biochemistry and clinical relevance of the isoprostane pathway. Lipids. 2005;40:987–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

