The Vibrio cholerae trh gene is coordinately regulated in vitro with type III secretion system genes by VttR(A)/VttR(B) but does not contribute to Caco2-BBE cell cytotoxicity
- PMID: 23045478
- PMCID: PMC3497436
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00832-12
The Vibrio cholerae trh gene is coordinately regulated in vitro with type III secretion system genes by VttR(A)/VttR(B) but does not contribute to Caco2-BBE cell cytotoxicity
Abstract
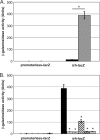
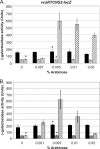
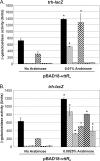
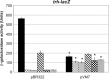
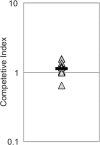
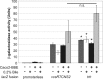
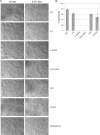
Numerous virulence factors have been associated with pathogenic non-O1/non-O139 serogroup strains of Vibrio cholerae. Among them are the thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH) and the TDH-related hemolysin (TRH), which share amino acid similarities to the TDH and TRH proteins of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, where they have been shown to contribute to pathogenesis. Although TDH and TRH homologs can be encoded on extrachromosomal elements in V. cholerae, type III secretion system (T3SS)-positive strains, such as AM-19226, carry a copy of trh within the T3SS genomic island. Transcriptional fusion analysis showed that in strain AM-19226, trh expression is regulated in a bile-dependent manner by a family of transmembrane transcriptional regulators that includes VttR(A), VttR(B), and ToxR. Genes encoding T3SS structural components are expressed under similar conditions, suggesting that within the T3SS genomic island, genes encoding proteins unrelated to the T3SS and loci involved in T3SS synthesis are coregulated. Despite similar in vitro expression patterns, however, TRH is not required for AM-19226 to colonize the infant mouse intestine, nor does it contribute to bile-mediated cytotoxicity when strain AM-19226 is cocultured with the mammalian cell line Caco2-BBE. Instead, we found that a functional T3SS is essential for AM-19226 to induce bile-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Collectively, the results are consistent with a more minor role for the V. cholerae TRH in T3SS-positive strains compared to the functions attributed to the V. parahaemolyticus TDH and TRH proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation by ToxR-Like Proteins Converges on vttRB Expression To Control Type 3 Secretion System-Dependent Caco2-BBE Cytotoxicity in Vibrio cholerae.J Bacteriol. 2016 May 13;198(11):1675-1682. doi: 10.1128/JB.00130-16. Print 2016 Jun 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27021561 Free PMC article.
-
vttRA and vttRB Encode ToxR family proteins that mediate bile-induced expression of type three secretion system genes in a non-O1/non-O139 Vibrio cholerae strain.Infect Immun. 2010 Jun;78(6):2554-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01073-09. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20385759 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Vibrio cholerae type III secretion system effector proteins.Infect Immun. 2011 Apr;79(4):1728-40. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01194-10. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21282418 Free PMC article.
-
Diarrhea induced by infection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus.J Med Invest. 2010 Aug;57(3-4):179-82. doi: 10.2152/jmi.57.179. J Med Invest. 2010. PMID: 20847516 Review.
-
[Type III secretion system of Vibrio parahaemolyticus--a review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2009 Jul;49(7):848-52. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 19873746 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
An essential host dietary fatty acid promotes TcpH inhibition of TcpP proteolysis promoting virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae.mBio. 2024 Aug 14;15(8):e0072124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00721-24. Epub 2024 Jul 3. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38958446 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of V. cholerae T3SS-dependent cytotoxicity in cultured intestinal epithelial cells.Cell Microbiol. 2016 Dec;18(12):1857-1870. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12629. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Cell Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27302486 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of the Fittest: How Bacterial Pathogens Utilize Bile To Enhance Infection.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Oct;29(4):819-36. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00031-16. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27464994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transmembrane Transcription Regulators Are Widespread in Bacteria and Archaea.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0026623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00266-23. Epub 2023 May 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37154724 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic and in silico functional analyses of thermostable-direct hemolysin and tdh-related encoding genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus and other Gram-negative bacteria.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:576528. doi: 10.1155/2014/576528. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25114910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403–410 - PubMed
-
- Baba K, Yamasaki S, Nishibuchi M, Takeda Y. 1992. Examination by site-directed mutagenesis of the amino acid residues of the thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus required for its hemolytic activity. Microb. Pathog. 12:279–287 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

