Effects of statins and farnesyl transferase inhibitors on ERK phosphorylation, apoptosis and cell viability in non-small lung cancer cells
- PMID: 23045963
- PMCID: PMC6496308
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2012.00846.x
Effects of statins and farnesyl transferase inhibitors on ERK phosphorylation, apoptosis and cell viability in non-small lung cancer cells
Abstract
Objective: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors (statins) can affect post-translational processes, thus being responsible for decreased farnesylation and geranylgeranylation of intracellular small G proteins such as Ras, Rho and Rac, essential for cell survival and proliferation. In this regard, recent in vitro and in vivo studies suggest a possible role for both statins and farnesyl transferase inhibitors in the treatment of malignancies. Within such a context, the aim of our study was to investigate effects of either simvastatin (at concentrations of 1, 15, and 30 μm) or the farnesyl transferase inhibitor R115777 (at concentrations of 0.1, 1, and 10 μm), on two cultures of human non-small lung cancer cells, adenocarcinoma (GLC-82) and squamous (CALU-1) cell lines. In particular, we evaluated actions of these two drugs on phosphorylation of the ERK1/2 group of mitogen-activated protein kinases and on apoptosis, plus on cell numbers and morphology.
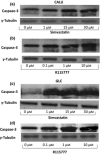
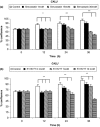
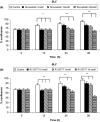
Materials and methods: Western blotting was used to detect ERK phosphorylation, and to assess apoptosis by evaluating caspase-3 activation; apoptosis was also further assessed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl-mediated dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) assay. Cell counting was performed after trypan blue staining.
Results and conclusion: In both GLC-82 and CALU-1 cell lines, simvastatin and R115777 significantly reduced ERK phosphorylation; this effect, which reached the greatest intensity after 36 h treatment, was paralleled by a concomitant induction of apoptosis, documented by significant increase in both caspase-3 activation and TUNEL-positive cells, associated with a reduction in cell numbers. Our results thus suggest that simvastatin and R115777 may exert, in susceptible lung cancer cell phenotypes, a pro-apoptotic and anti-proliferative activity, which appears to be mediated by inhibition of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signalling cascade.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of simvastatin on cell viability and proinflammatory pathways in lung adenocarcinoma cells exposed to hydrogen peroxide.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014 Nov 29;15:67. doi: 10.1186/2050-6511-15-67. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25432084 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin interacts synergistically with tipifarnib to induce apoptosis in leukemia cells through the disruption of RAS membrane localization and ERK pathway inhibition.Leuk Res. 2014 Nov;38(11):1350-7. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Leuk Res. 2014. PMID: 25262449 Free PMC article.
-
Farnesyl transferase inhibitor (R115777)-induced inhibition of STAT3(Tyr705) phosphorylation in human pancreatic cancer cell lines require extracellular signal-regulated kinases.Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 1;65(7):2861-71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2396. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15805288
-
Farnesyl transferase inhibitors for patients with lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jun 15;10(12 Pt 2):4254s-4257s. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-040016. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15217969 Review.
-
Effects of statins and farnesyltransferase inhibitors on the development and progression of cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2004 Nov;30(7):609-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2004.06.010. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004. PMID: 15531395 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluvastatin influences hair color in C57BL/6 mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 10;14(7):14333-45. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714333. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23846727 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol-4-O-D-(2'-galloyl)-glucopyranoside isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum exhibits anti-hepatocellular carcinoma viability by inducing apoptosis via the JNK and ERK pathway.Molecules. 2014 Jan 27;19(2):1592-602. doi: 10.3390/molecules19021592. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24473215 Free PMC article.
-
Statins as potential adjuvant therapy in lung cancer: a narrative review.J Thorac Dis. 2025 May 30;17(5):3433-3449. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2025-66. Epub 2025 May 19. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40529769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational design, chemical synthesis, and biological evaluation of a novel ERK inhibitor (BL-EI001) with apoptosis-inducing mechanisms in breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 30;6(9):6762-75. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3105. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25742792 Free PMC article.
-
Cilostazol prevents foot ulcers in diabetic patients with peripheral vascular disease.Int Wound J. 2015 Jun;12(3):250-3. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12085. Epub 2013 May 15. Int Wound J. 2015. PMID: 23672237 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

