Structural and dynamic determinants of type I interferon receptor assembly and their functional interpretation
- PMID: 23046138
- PMCID: PMC3986811
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.12001
Structural and dynamic determinants of type I interferon receptor assembly and their functional interpretation
Abstract
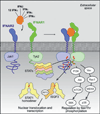
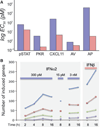
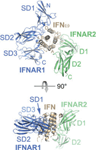
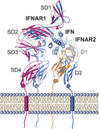
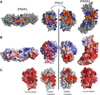
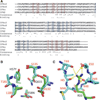
Type I interferons (IFNs) form a network of homologous cytokines that bind to a shared, heterodimeric cell surface receptor and engage signaling pathways that activate innate and adaptive immune responses. The ability of IFNs to mediate differential responses through the same cell surface receptor has been subject of a controversial debate and has important medical implications. During the past decade, a comprehensive insight into the structure, energetics, and dynamics of IFN recognition by its two-receptor subunits, as well as detailed correlations with their functional properties on the level of signal activation, gene expression, and biological responses were obtained. All type I IFNs bind the two-receptor subunits at the same sites and form structurally very similar ternary complexes. Differential IFN activities were found to be determined by different lifetimes and ligand affinities toward the receptor subunits, which dictate assembly and dynamics of the signaling complex in the plasma membrane. We present a simple model, which explains differential IFN activities based on rapid endocytosis of signaling complexes and negative feedback mechanisms interfering with ternary complex assembly. More insight into signaling pathways as well as endosomal signaling and trafficking will be required for a comprehensive understanding, which will eventually lead to therapeutic applications of IFNs with increased efficacy.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

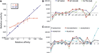
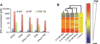

References
-
- Stetson DB, Medzhitov R. Type I interferons in host defense. Immunity. 2006;25:373–381. - PubMed
-
- Isaacs A, Lindenmann J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957;147:258–267. - PubMed
-
- Uze G, Lutfalla G, Gresser I. Genetic transfer of a functional human interferon alpha receptor into mouse cells: cloning and expression of its cDNA. Cell. 1990;60:225–234. - PubMed
-
- Novick D, Cohen B, Rubinstein M. The human interferon alpha/beta receptor: characterization and molecular cloning. Cell. 1994;77:391–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

