Understanding cytokine and growth factor receptor activation mechanisms
- PMID: 23046381
- PMCID: PMC3537265
- DOI: 10.3109/10409238.2012.729561
Understanding cytokine and growth factor receptor activation mechanisms
Abstract
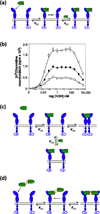
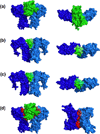
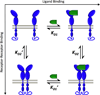
Our understanding of the detailed mechanism of action of cytokine and growth factor receptors - and particularly our quantitative understanding of the link between structure, mechanism and function - lags significantly behind our knowledge of comparable functional protein classes such as enzymes, G protein-coupled receptors, and ion channels. In particular, it remains controversial whether such receptors are activated by a mechanism of ligand-induced oligomerization, versus a mechanism in which the ligand binds to a pre-associated receptor dimer or oligomer that becomes activated through subsequent conformational rearrangement. A major limitation to progress has been the relative paucity of methods for performing quantitative mechanistic experiments on unmodified receptors expressed at endogenous levels on live cells. In this article, we review the current state of knowledge on the activation mechanisms of cytokine and growth factor receptors, critically evaluate the evidence for and against the different proposed mechanisms, and highlight other key questions that remain unanswered. New approaches and techniques have led to rapid recent progress in this area, and the field is poised for major advances in the coming years which promise to revolutionize our understanding of this large and biologically and medically important class of receptors.
Figures










References
-
- Adar R, Monsonego-Ornan E, David P, Yayon A. Differential activation of cysteine-substitution mutants of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is determined by cysteine localization. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(5):860–868. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M. The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3(5):383–394. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen MS, Titievsky A, et al. GDNF family neurotrophic factor signaling: four masters, one servant? Mol Cell Neurosci. 1999;13(5):313–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
