Alteration of endothelial function markers in women with gestational diabetes and their fetuses
- PMID: 23046386
- PMCID: PMC3622728
- DOI: 10.3109/14767058.2012.736564
Alteration of endothelial function markers in women with gestational diabetes and their fetuses
Abstract
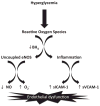
Objective: We tested the hypothesis that women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and their fetuses would demonstrate alterations in markers of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) uncoupling, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction and these changes would correlate with the levels of hyperglycemia through a pilot observational case-control study of women with GDM and their fetuses.
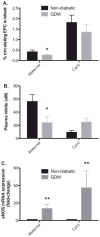
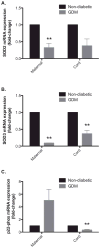
Methods: Levels of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (sVCAM-1), C-reactive protein (CRP), nitric oxide (NO), eNOS, p22-phox, and SOD gene expression, and endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) counts in both maternal and cord blood were measured at the time of delivery in women with and without GDM.
Results: We demonstrated the presence of decreased maternal circulating EPC counts, increased soluble adhesion molecules in maternal blood, decreased SOD expression in both maternal and cord blood and increased eNOS expression in both maternal and cord blood in women with GDM.
Conclusions: These data suggest that the molecular mechanisms behind oxidative stress in women with GDM and their fetuses appear similar to those hypothesized for non-pregnant adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
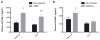
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, et al. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics–2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:948–954. - PubMed
-
- de Jager J, Dekker JM, Kooy A, Kostense PJ, Nijpels G, Heine RJ, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CD. Endothelial dysfunction and low-grade inflammation explain much of the excess cardiovascular mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1086–1093. - PubMed
-
- Deanfield J, Donald A, Ferri C, Giannattasio C, Halcox J, Halligan S, Lerman A, et al. Working Group on Endothelin and Endothelial Factors of the European Society of Hypertension. Endothelial function and dysfunction. Part I: Methodological issues for assessment in the different vascular beds: a statement by the Working Group on Endothelin and Endothelial Factors of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2005;23:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Calles-Escandon J, Cipolla M. Diabetes and endothelial dysfunction: a clinical perspective. Endocr Rev. 2001;22:36–52. - PubMed
-
- Meigs JB, Hu FB, Rifai N, Manson JE. Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 2004;291:1978–1986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
