Prediction consistency and clinical presentations of breast cancer molecular subtypes for Han Chinese population
- PMID: 23046482
- PMCID: PMC3445863
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-S1-S10
Prediction consistency and clinical presentations of breast cancer molecular subtypes for Han Chinese population
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease in terms of transcriptional aberrations; moreover, microarray gene expression profiles had defined 5 molecular subtypes based on certain intrinsic genes. This study aimed to evaluate the prediction consistency of breast cancer molecular subtypes from 3 distinct intrinsic gene sets (Sørlie 500, Hu 306 and PAM50) as well as clinical presentations of each molecualr subtype in Han Chinese population.
Methods: In all, 169 breast cancer samples (44 from Taiwan and 125 from China) of Han Chinese population were gathered, and the gene expression features corresponding to 3 distinct intrinsic gene sets (Sørlie 500, Hu 306 and PAM50) were retrieved for molecular subtype prediction.
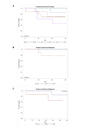
Results: For Sørlie 500 and Hu 306 intrinsic gene set, mean-centring of genes and distance-weighted discrimination (DWD) remarkably reduced the number of unclassified cases. Regarding pairwise agreement, the highest predictive consistency was found between Hu 306 and PAM50. In all, 150 and 126 samples were assigned into identical subtypes by both Hu 306 and PAM50 genes, under mean-centring and DWD. Luminal B tended to show a higher nuclear grade and have more HER2 over-expression status than luminal A did. No basal-like breast tumours were ER positive, and most HER2-enriched breast tumours showed HER2 over-expression, whereas, only two-thirds of ER negativity/HER2 over-expression tumros were predicted as HER2-enriched molecular subtype. For 44 Taiwanese breast cancers with survival data, a better prognosis of luminal A than luminal B subtype in ER-postive breast cancers and a better prognosis of basal-like than HER2-enriched subtype in ER-negative breast cancers was observed.
Conclusions: We suggest that the intrinsic signature Hu 306 or PAM50 be used for breast cancers in the Han Chinese population during molecular subtyping. For the prognostic value and decision making based on intrinsic subtypes, further prospective study with longer survival data is needed.
Figures
References
-
- Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lønning PE, Børresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–452. doi: 10.1038/35021093. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Lønning PE, Børresen-Dale AL. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:10869–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191367098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, Demeter J, Perou CM, Lønning PE, Brown PO, Børresen-Dale AL, Botstein D. Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:8418–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0932692100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu Z, Fan C, Oh DS, Marron JS, He X, Qaqish BF, Livasy C, Carey LA, Reynolds E, Dressler L, Nobel A, Parker J, Ewend MG, Sawyer LR, Wu J, Liu Y, Nanda R, Tretiakova M, Ruiz Orrico A, Dreher D, Palazzo JP, Perreard L, Nelson E, Mone M, Hansen H, Mullins M, Quackenbush JF, Ellis MJ, Olopade OI, Bernard PS, Perou CM. The molecular portraits of breast tumors are conserved across microarray platforms. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:96. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-96. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sotiriou C, Neo SY, McShane LM, Korn EL, Long PM, Jazaeri A, Martiat P, Fox SB, Harris AL, Liu ET. Breast cancer classification and prognosis based on gene expression profiles from a population-based study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:10393–10398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1732912100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

