The social brain in psychiatric and neurological disorders
- PMID: 23047070
- PMCID: PMC3606817
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tics.2012.09.006
The social brain in psychiatric and neurological disorders
Abstract
Psychiatric and neurological disorders have historically provided key insights into the structure-function relationships that subserve human social cognition and behavior, informing the concept of the 'social brain'. In this review, we take stock of the current status of this concept, retaining a focus on disorders that impact social behavior. We discuss how the social brain, social cognition, and social behavior are interdependent, and emphasize the important role of development and compensation. We suggest that the social brain, and its dysfunction and recovery, must be understood not in terms of specific structures, but rather in terms of their interaction in large-scale networks.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
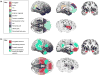



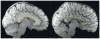
References
-
- Klin A, et al. Visual fixation patterns during viewing of naturalistic social situations as predictors of social competence in individuals with autism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2002;59:809–816. - PubMed
-
- Pelphrey KA, et al. Visual scanning of faces in autism. J Autism Dev Disord. 2002;32:249–261. - PubMed
-
- Spezio ML, et al. Analysis of face gaze in autism using ‘Bubbles’. Neuropsychologia. 2007;45:144–151. - PubMed
-
- Damasio AR, et al. Face agnosia and the neural substrates of memory. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:89–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

