The inoculum effect and band-pass bacterial response to periodic antibiotic treatment
- PMID: 23047527
- PMCID: PMC3472685
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2012.49
The inoculum effect and band-pass bacterial response to periodic antibiotic treatment
Abstract
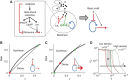
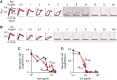
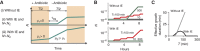
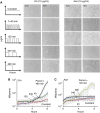
The inoculum effect (IE) refers to the decreasing efficacy of an antibiotic with increasing bacterial density. It represents a unique strategy of antibiotic tolerance and it can complicate design of effective antibiotic treatment of bacterial infections. To gain insight into this phenomenon, we have analyzed responses of a lab strain of Escherichia coli to antibiotics that target the ribosome. We show that the IE can be explained by bistable inhibition of bacterial growth. A critical requirement for this bistability is sufficiently fast degradation of ribosomes, which can result from antibiotic-induced heat-shock response. Furthermore, antibiotics that elicit the IE can lead to 'band-pass' response of bacterial growth to periodic antibiotic treatment: the treatment efficacy drastically diminishes at intermediate frequencies of treatment. Our proposed mechanism for the IE may be generally applicable to other bacterial species treated with antibiotics targeting the ribosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Balenci D, Bernardi F, Cellai L, D'Amelio N, Gaggelli E, Gaggelli N, Molteni E, Valensin G (2008) Effect of Cu-II on the complex between kanamycin A and the bacterial ribosomal A site. Chembiochem 9: 114–123 - PubMed
-
- Bayles KW (2007) The biological role of death and lysis in biofilm development. Nat Rev Microbiol 5: 721–726 - PubMed
-
- Bota DA, Davies KJ (2002) Lon protease preferentially degrades oxidized mitochondrial aconitase by an ATP-stimulated mechanism. Nat Cell Biol 4: 674–680 - PubMed
-
- Brook I (1989) Inoculum effect. Rev Infect Dis 11: 361–368 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

