Distinct and replicable genetic risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome of pulmonary or extrapulmonary origin
- PMID: 23048207
- PMCID: PMC3654537
- DOI: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-100972
Distinct and replicable genetic risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome of pulmonary or extrapulmonary origin
Abstract
Background: The role of genetics in the development of acute lung injury (ALI)/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) from direct or indirect lung injury has not been specifically investigated. The aim of this study was to identify genetic variants contributing to ALI/ARDS from pulmonary or extrapulmonary causes.
Methods: We conducted a multistage genetic association study. We first performed a large-scale genotyping (50K ITMAT-Broad_CARe Chip) in 1717 critically ill Caucasian patients with either pulmonary or extrapulmonary injury, to identify single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with the development of ARDS from direct or indirect insults to the lung. Identified SNPs (p≤0.0005) were validated in two separated populations (Stage II), with trauma (Population I; n=765) and pneumonia/pulmonary sepsis (Population II; n=838), as causes for ALI/ARDS. Genetic variants replicating their association with trauma related-ALI in Stage II were validated in a second trauma-associated ALI population (n=224, Stage III).
Results: In Stage I, non-overlapping SNPs were significantly associated with ARDS from direct/indirect lung injury, respectively. The association between rs1190286 (POPDC3) and reduced risk of ARDS from pulmonary injury was validated in Stage II (p<0.003). SNP rs324420 (FAAH) was consistently associated with increased risk of ARDS from extrapulmonary causes in two independent ALI-trauma populations (p<0.006, Stage II; p<0.05, Stage III). Meta-analysis confirmed these associations.
Conclusions: Different genetic variants may influence ARDS susceptibility depending on direct versus indirect insults. Functional SNPs in POPDC3 and FAAH genes may be driving the association with direct and indirect ALI/ARDS, respectively.
Figures
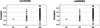
References
-
- Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, Legall JR, Morris A, Spragg R. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149(3 Pt 1):818–824. - PubMed
-
- Artigas A, Bernard GR, Carlet J, Dreyfuss D, Gattinoni L, Hudson L, Lamy M, Marini JJ, Matthay MA, Pinsky MR, Spragg R, Suter PM. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS, part 2: Ventilatory, pharmacologic, supportive therapy, study design strategies, and issues related to recovery and remodeling. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(4 Pt 1):1332–1347. - PubMed
-
- Rocco PR, Pelosi P. Pulmonary and extrapulmonary acute respiratory distress syndrome: myth or reality? Curr Opin Crit Care. 2008;14(1):50–55. - PubMed
-
- Desai SR, Wells AU, Rubens MB, Evans TW, Hansell DM. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: CT abnormalities at long-term follow-up. Radiology. 1999;210(1):29–35. - PubMed
-
- Goodman LR, Fumagalli R, Tagliabue P, Tagliabue M, Ferrario M, Gattinoni L, Pesenti A. Adult respiratory distress syndrome due to pulmonary and extrapulmonary causes: CT, clinical, and functional correlations. Radiology. 1999;213(2):545–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
